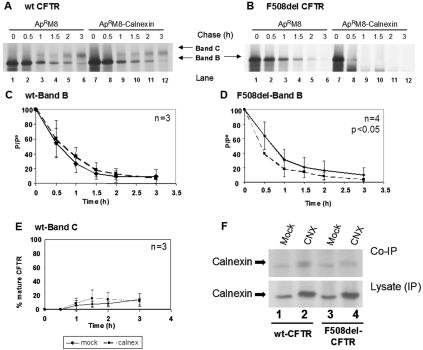
FIG. 2.
Turnover and processing of wt and F508del-CFTR under calnexin overexpression. CHO cells stably expressing (A) wt or (B) F508del-CFTR were transiently transfected with the calnexin cDNA construct (lanes 7 to 12) or with the same amount of empty vector as a control (lanes 1 to 6). Twenty-four hours posttransfection, the cells were pulse-labeled for 30 min with [35S]methionine and chased for 0 h (lanes 1 and 7), 0.5 h (lanes 2 and 8), 1 h (lanes 3 and 9), 1.5 h (lanes 4 and 10), 2 h (lanes 5 and 11), and 3 h (lanes 6 and 12). The cells were then lysed and immunoprecipitated with an anti-CFTR Ab (see Materials and Methods). Following electrophoretic separation and fluorography, immature (band B) and mature (band C) forms of CFTR were quantified (see Materials and Methods). Turnover of the core-glycosylated form (band B) of wt CFTR (C) and F508del-CFTR (D) is shown as the ratio between P, the amount of band B at time t, and P0, the amount of band B at the start of the chase (i.e., at the end of pulse). The efficiency of conversion of the core-glycosylated form (band B) into the fully glycosylated form of wt CFTR (band C) was also estimated for wt CFTR (E) and was determined as the ratio between the amount of band C at time t and the amount of band B at the start of the chase (P0). The number of experiments is indicated at the right upper corner of panels C, D, and E. Statistically significant differences are indicated (P < 0.05). (F) (Top) Calnexin cDNA was used to transfect cells stably expressing wt or F508del-CFTR. After being labeled with [35S]methionine, the cells were lysed and CFTR immunoprecipitated with an anti-CFTR Ab. After elution, a second IP was performed (see Materials and Methods) using a mixture (1:1) of human and hamster anticalnexin Abs. Lanes 1 and 3, cells transfected with empty vector (as a control); lanes 2 and 4, cells transfected with calnexin cDNA. (Bottom) Results of direct IP of calnexin in lysates.