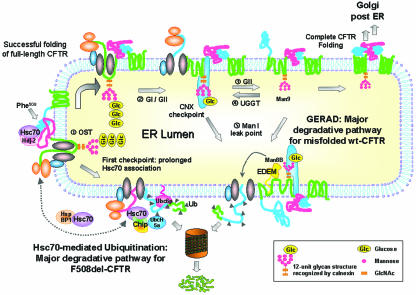
FIG. 9.
Proposed model for the major degradation pathways of F508del- and wt CFTR. (i) Synthesis of CFTR occurs with its concomitant insertion in the ER membrane and attachment of an Hsc70/Hdj-2 (or Hsp70/Hdj-1) pair to nascent cytosolic domains, as described previously (12, 30). Other authors have described increased levels of Hsc70/Hdj-2 complexes with F508del-CFTR relative to wt CFTR and expression of NBD1 as the earliest point at which Hsc70/Hdj-2 could bind the nascent CFTR polypeptidic chain (30). The same study reported that complex formation between Hdj-2 and nascent wt CFTR was greatly reduced after expression of the R domain, suggesting NBD1-R domain interaction as a critical point in CFTR folding. The cell thus seems to use this Hsc70/Hsp70 control as the first checkpoint to assess CFTR conformation, and we propose that it is the major mechanism to discard F508del-CFTR. Prolonged retention of unfolded F508del-CFTR by Hsc70 at this point enables CHIP to interact with Hsc70/Hsp70 (probably by displacing Hdj-2) and causes the mutant to be degraded through the Hsc70-CHIP-UbcH5a pathway (31, 57). The E2 Ubc6 may also contribute to F508del-CFTR ERAD (24). Contrary to what happens with F508del-CFTR, wt CFTR, for which NBD1-R intramolecular interaction and folding is achieved, proceeds in the folding pathway through interaction of its N-glycosyl residues (ii) with calnexin (iii). Wt CFTR acquires its native conformation through successive rounds of release-deglucosylation (iv) and rebinding-reglucosylation (v) to calnexin, which also constitutes the second ERQC checkpoint. Upon successful folding, CFTR exits the ER, proceeding through the secretory pathway (vi). However, prolonged presence in the calnexin cycle may cause misfolded CFTR to become a substrate of mannosidase I (vii). This enzyme trims mannose residues from the protein glycan moiety, possibly generating the Man8B glycan intermediate that is recognized by EDEM, which targets the client protein to ERAD (viii). We call this ER-degradative pathway GERAD, to indicate its dependence on the glycan moiety. According to this model, F508del-CFTR follows a major degradative pathway from the first (Hsc70-dependent) ERQC checkpoint, whereas misfolded wt CFTR undergoes proteolytic GERAD at the second (calnexin-dependent) one (see the text for a description).