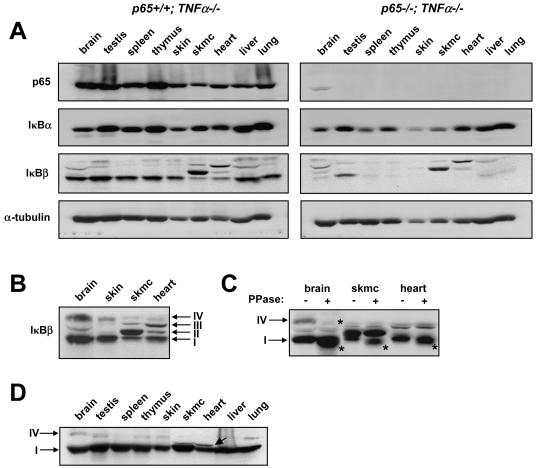
FIG. 3.
p65 regulates various forms of IκBβ in postnatal development in a tissue-specific manner. p65+/− TNF-α−/− mice were bred to generate p65+/+ TNF-α−/− and p65−/− TNF-α−/− progeny. (A) At 4 weeks of age, mice were sacrificed and tissue homogenates were prepared (skmc, skeletal muscle). Western blot assays were then performed to probe for p65, IκBα, IκBβ, and α-tubulin. Each Western blot assay is representative of a total of four different blot assays derived from two sets of littermates. (B) Western blot assay to probe for IκBβ in p65+/+ TNF-α−/− brain, skin, skeletal muscle, and heart tissues. Arrows denote IκBβ forms I through IV. (C) Similar extracts as in panel A were either left untreated or treated with phosphatase (PPase) enzyme, and Western blot assay was performed to probe for IκBβ. Arrows denote phosphorylated forms of IκBβ, and asterisks denote the shifted (dephosphorylated) forms of IκBβ. (D) The N-terminal IκBβ antibody (N20) was used in a Western analysis to verify IκBβ forms in p65+/+ TNF-α−/− tissues.