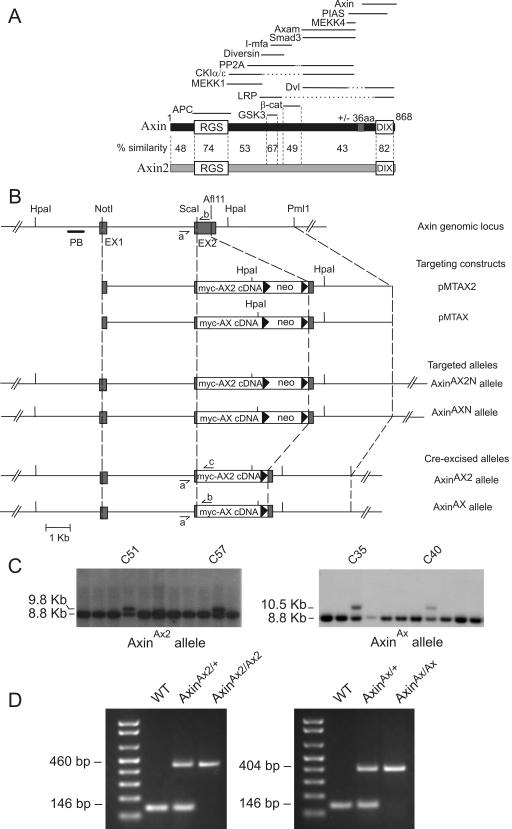
FIG.1.
Targeted replacement of the Axin gene with myc-tagged Axin2 cDNA or myc-tagged Axin cDNA. (A) Schematic diagram of Axin and Axin2 proteins and binding partners. Percent similarities between the conserved RGS and DIX domains and the GSK3 and β-catenin (β-cat) binding regions of Axin and Axin2 are indicated, as are those of other less-conserved regions. The solid lines at the top indicate the regions of Axin involved in binding to the indicated proteins (31). Of these, only APC, GSK3, β-catenin, Diversin, and Smad3 are known to bind to Axin2. aa, amino acids; PP2A, protein phosphatase 2A. (B) Schematic diagram of the Axin genomic locus, targeting constructs, and targeted alleles. Exons 1 and 2 (EX1 and EX2) are depicted as grey boxes, and intron sequences are depicted as solid lines. The positions of the restriction enzyme sites and the probe PB are indicated. Small harpoons (⇁ and ↼) show the PCR primers AXL1 (a), MTAXR1 (b), and MTCONR1 (c). (C) Southern blot analysis of G418-resistant colonies after electroporation of ES cells with targeting constructs. Probing with probe PB following digestion of DNA with Hpa1 detected a band of 9.8 kb for the AxinAX2 allele, a band of 10.5 kb for the AxinAX allele, and a band of 8.8 kb for the wild-type allele. (D) Identification of homozygous, heterozygous, and wild-type (WT) AxinAX2 and AxinAX mice by PCR.