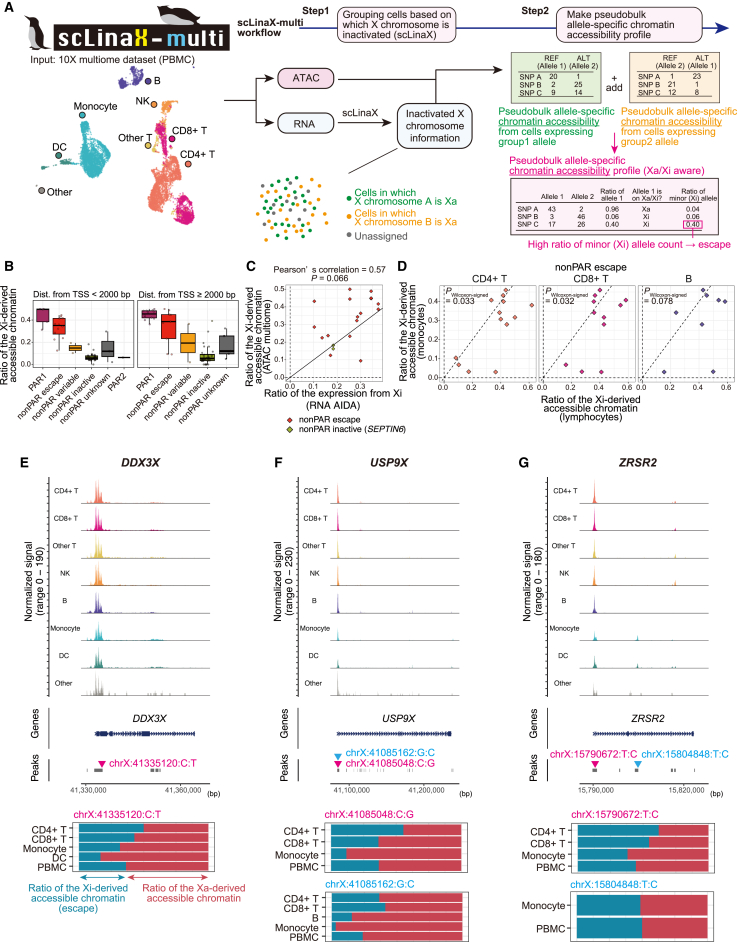
Figure 4.
scLinaX-multi, a method to estimate the chromatin accessibility of Xi from multi-modal single-cell omics data
(A) A schematic illustration of the scLinaX-multi (Data S4; STAR Methods).
(B) Boxplots represent the estimated ratio of the accessible chromatin derived from Xi for peaks within 2 kbp of TSS (left) and ≥2 kbp distant from TSS (right). Peaks are grouped according to the XCI status of the nearest gene.
(C) A plot representing the relationship between the ratio of the expression from Xi (RNA level, x axis) and the ratio of the accessible chromatin derived from Xi (y axis) for each peak-nearest gene pair. Genes that are annotated as escape genes or showed evidence of escape in the scLinaX analysis (ratio of the expression from Xi > 0.15) are indicated. The black line indicates x = y. When a single gene has multiple peaks, the average across the peaks for the ratio of the Xi-derived accessible chromatin is used for the calculation of Pearson’s correlation.
(D) Scatterplots represent pairwise comparisons of the accessible chromatin derived from Xi for peaks whose nearest genes are escapee genes. The y axes represent the ratio of the expression from Xi in monocytes and the x axes represent the ratio of the expression from Xi in lymphocytes. The dashed lines represent x = 0, x = y, and y = 0. The p values are calculated by the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
(E–G) The results of the scLinaX-multi for the representative peaks around escapee genes, namely DDX3X (E), USP9X (F), and ZRSR2 (G). Normalized tag counts across cell types are indicated with peak information (top). The ratio of the accessible chromatin derived from Xa and Xi across cell types is indicated as bar plots (bottom) with information on which SNPs are used for the analysis. Since the definition of alleles derived from Xa and Xi is consistent within the same individual, the ratio of expression from Xi may exceed 0.5 in some cell types. ATAC, assay for transposase-accessible chromatin; TSS, transcription start site.