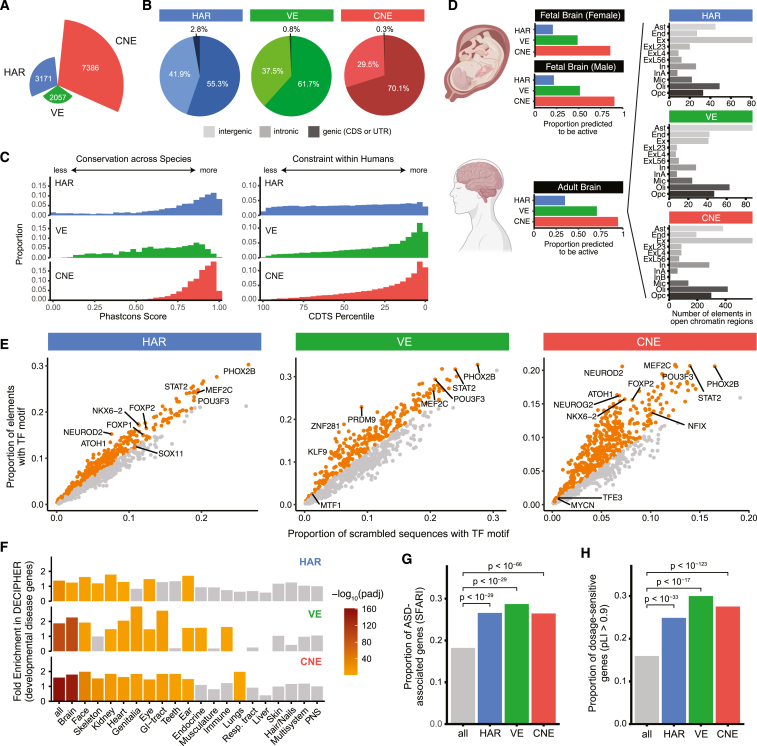
Figure 1.
Genomic and epigenomic features of HARs, VEs, and CNEs
(A) Numbers of HARs, VEs, and CNEs.
(B) Proportions of HARs, VEs, and CNEs in intergenic (light coloring), intronic (moderate coloring), and genic (dark coloring) regions.
(C) Conservation across species (left) and constraint within humans (right) are represented by phastCons score31 and CDTS percentile,32 respectively.
(D) Proportions of HARs, VEs, and CNEs predicted to be active by ChromHMM based on epigenomic data from a fetal male brain, a fetal female brain, and an adult brain30 (left). Numbers of HARs, VEs, and CNEs that overlap open chromatin regions from single-cell transposome hypersensitive site sequencing (scTHS-seq) across cell types in the adult brain33 (right). Ast, astrocytes; End, endothelial cells; Ex, excitatory neurons; ExL23, layers 2–3 excitatory neurons; ExL4, layer 4 excitatory neurons; ExL56, layers 5–6 excitatory neurons; In, inhibitory neurons; InA, inhibitory neurons subtype A; InB, inhibitory neurons subtype B; Mic, microglia; Oli, oligodendrocytes; Opc, oligodendrocyte precursor cells.
(E) Enrichment of TF-binding-site motifs in HARs, VEs, and CNEs (STAR Methods). Orange dots indicate significantly enriched elements, as assessed with the hypergeometric test at 5% false discovery rate (FDR).
(F) Enrichment of HARs, VEs, and CNEs near genes associated with developmental diseases in different body systems from the DECIPHER Consortium34 by the binomial test at 5% FDR.
(G) HARs, VEs, and CNEs are enriched for ASD-associated genes annotated in the SFARI database8 by the binomial test at 5% FDR.
(H) Genes near HARs, VEs, or CNEs are enriched for genes with pLI >0.9 (loss-of-function intolerant)35 by the hypergeometric test at 5% FDR.
Full details of statistical analyses are in STAR Methods.