Fig. 1.
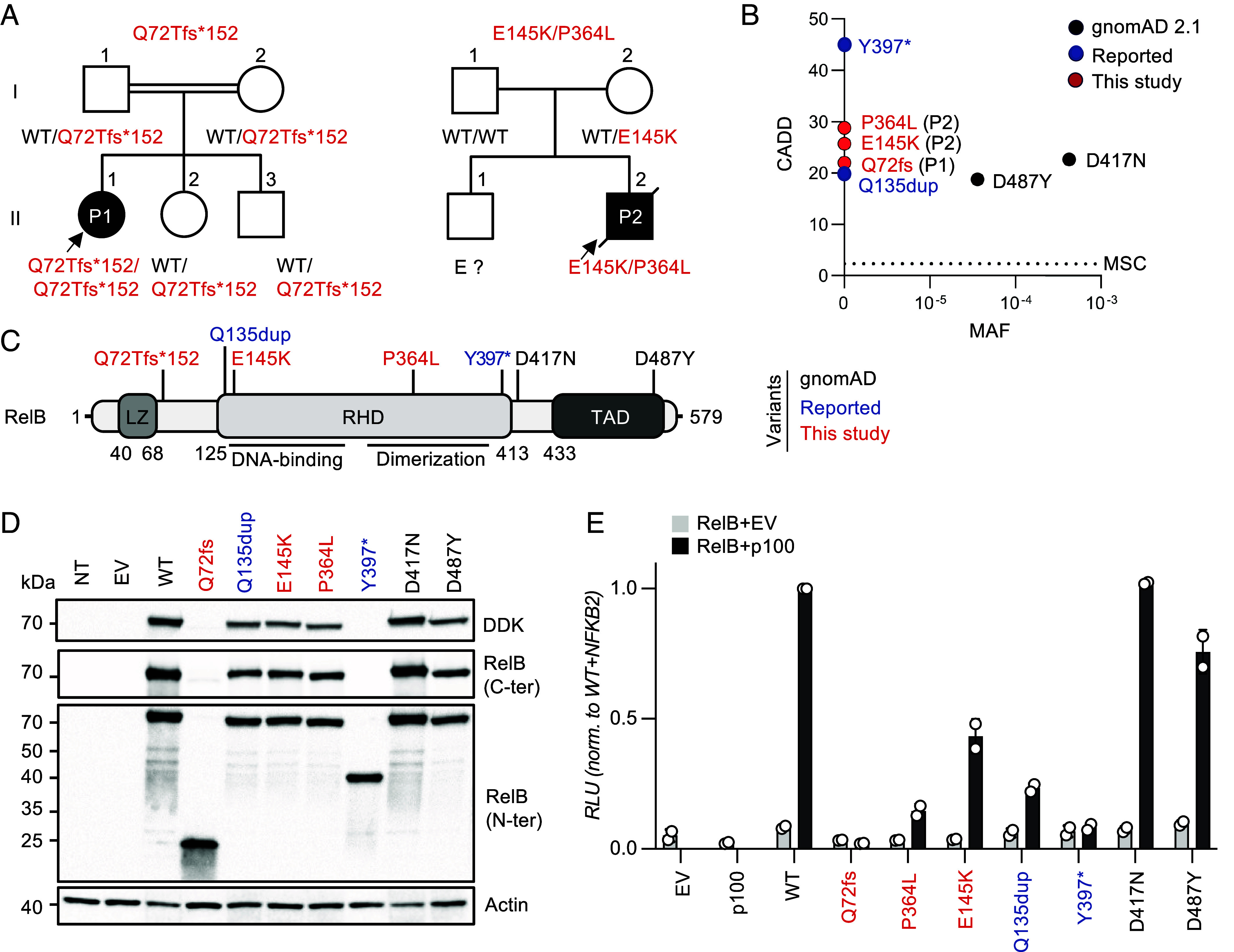
AR RelB deficiency in two unrelated patients. (A) Pedigrees of the two unrelated families. The familial segregation of the variants identified in P1 and P2 is depicted. The double lines connecting P1’s parents indicate consanguinity. An arrow indicates the probands. Solid symbols indicate disease status. “E?” indicates individuals of unknown genotype. (B) The CADD score and MAF of the variants of P1 and P2 (shown in red), the two previously reported disease-causing variants (shown in blue) (7, 23, 24), and the two homozygous missense variants found in the gnomAD 2.1 database (shown in black). All variants from P1, P2, and the four previously reported patients are private. The variants are plotted according to their CADD scores (y-axis) and MAF (x-axis). The black horizontal dotted line indicates the MSC. (C) Schematic diagram of the RelB protein. The regions corresponding to functionally significant domains are shown in dark gray (LZ: leucine zipper domain; RHD: Rel homology domain; TAD: transactivation domain). The variants of P1 and P2 are shown in red; the two previously reported disease-causing variants are indicated in blue, and the variants reported in the homozygous state in gnomAD appear in black. (D) Immunoblot analysis of RelB expression on total protein extracts from non-transfected HEK 293 T (NT) cells, or HEK 293 T cells transfected with an empty pCMV6 plasmid (EV), or pCMV6 plasmids containing the WT, P1’s variant (c.C212dup, p.Q72Tfs*152, or p.Q72fs), P2’s variant (c.433G>A/c.1091C>T, p.E145K/p.P364L), the previously reported disease-causing variants (c.1191C>A, p.Y397*, and c.400_c.401insAGC/p.Q135dup), or the two missense (c.1249G>A, p.D417N, and c.1459G>T, p.D487Y) variants of RELB present in the homozygous state in gnomAD. RelB was detected with a mAb specific for the C- or N-terminal region or with an antibody against the DDK tag. Actin was used as a loading control. The results shown are representative of three independent experiments. (E) Luciferase activity of HEK 293 T cells after 48 h of transfection with an NF-κB reporter plasmid together with an empty pCMV6 vector (EV), or a pCMV6 vector encoding wild-type (WT), P1’s variant (c.C212dup/p.Q72Tfs*152), P2’s variant (c.433G>A/p.E145K and c.1091C>T/p.P364L), the previously reported disease-causing (c.1191 C>A/p.Y397* and c.400_c.401insAGC/p.Q135dup) variants, and the two missense (c.1249 G > A/p.D417N; c.1459 G>T/p.D487Y) RelB variants present in the homozygous state in gnomAD, with or without the pCMV6-NFKB2-DDK plasmid encoding p100. Results were normalized against Renilla luciferase activity. Results were then normalized against the level of transcriptional activity for the WT p52/RelB dimer. The mean ± SD of one representative experiment (performed with a biological duplicate) is shown.
