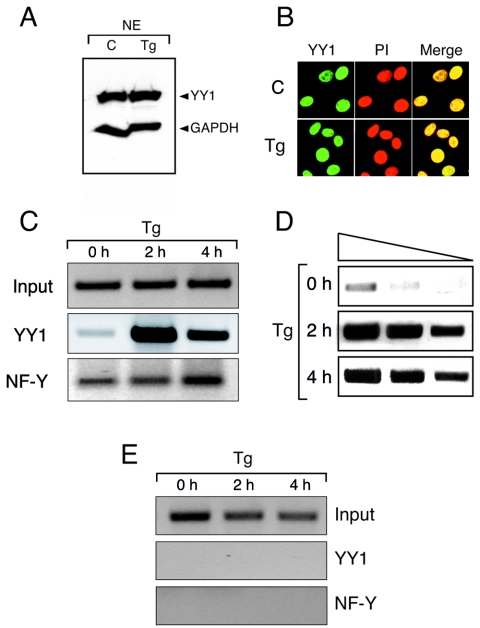
FIG. 2.
ER stress-induced YY1 binding to the Grp78 promoter in vivo. (A) A total of 20 μg of HeLa nuclear extract from control and cells treated with Tg for 16 h was loaded onto a SDS-polyacrylamide gel, and the subsequent blot was reacted with anti-YY1 polyclonal and anti-GAPDH monoclonal antibodies. (B) NIH 3T3 cells were grown to 50% confluence in chamber slides and treated as indicated with 300 nM Tg for 8 h. The cells were fixed and stained with anti-YY1 monoclonal antibody and counterstained with propidium iodide. The cells were visualized with a Zeiss LSM510 confocal microscope (magnification, ×300). (C) NIH 3T3 cells were grown to 80 to 90% confluence; treated with 300 nM Tg for 0, 2, or 4 h; and then cross-linked with 1% formaldehyde. Chromatin extracts were prepared, and immunoprecipitation reactions were carried out with antibodies against YY1 or NF-Y. After reversal of cross-links, DNA was subjected to PCRs to amplify a 223-bp region of the Grp78 promoter. (D) Threefold dilutions of the DNA from the YY1 ChIP assay as shown in panel C were subjected to PCR for confirmation of linear range. (E) DNA collected from the YY1 and NF-Y ChIP assays were subjected to PCR with primers for a 248-bp region of the Grp78 exon VIII coding region.