Fig. 2 ∣. A schematic illustration of the principle and protocol of SCMDA.
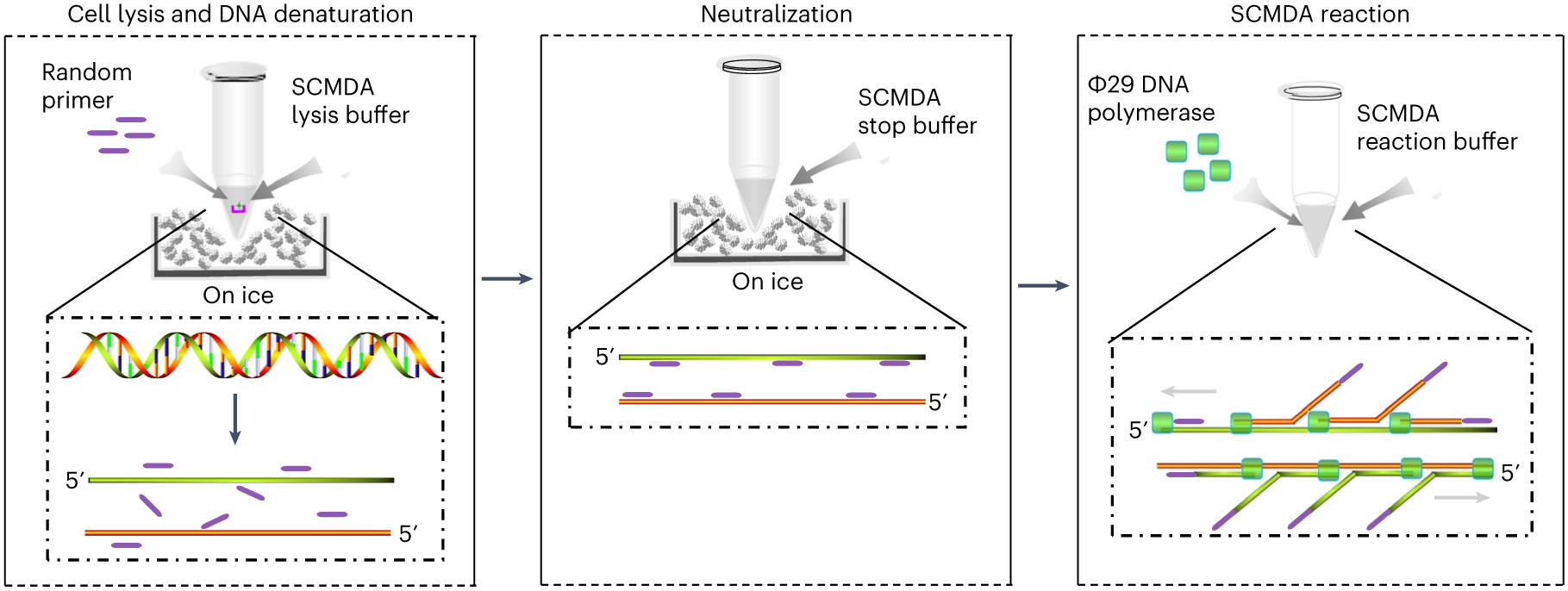
SCMDA includes three major stages: cell lysis and DNA denaturation (left), neutralization (middle) and SCMDA reaction (right). Cell lysis and DNA denaturation: a single cell (represented by a green star) on a cellraft (represented by a pink u-shape symbol) is collected into a PCR tube and placed on ice. Random primers (represented by a purple line) and SCMDA lysis buffer are added into the tube to start cell lysis and DNA denaturation on ice. Neutralization: SCMDA stop buffer is added into the PCR tube to neutralize the reaction of cell lysis and DNA denaturation. Random primers bind to single-strand DNA and prevent renaturation of the two original DNA strands. SCMDA reaction: Φ29 DNA polymerase (represented by a green square) and SCMDA reaction buffer are added into the PCR tube for SCMDA.
