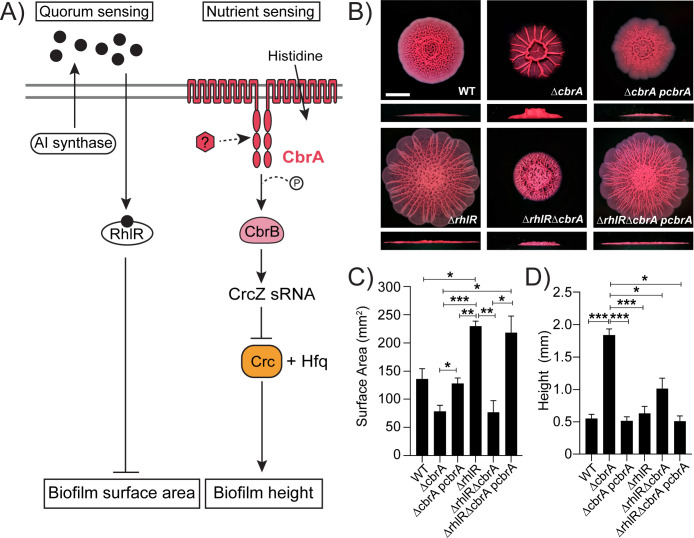
Fig 1.
P. aeruginosa ΔcbrA and ΔrhlR mutants have distinct hyper-rugose biofilm phenotypes. (A) Schematic of the RhlR quorum sensing and CbrA nutrient sensing pathways. The two gray horizontal lines represent the cytoplasmic membrane, black circles represent autoinducer sensed by RhlR, red hexagon represents the unknown signal that activates CbrA sensor kinase. CbrA also functions as a histidine transporter, but its kinase function appears to be independent of histidine transport (17). (B) Colony biofilm phenotypes of WT PA14 and the designated mutants on Congo red agar medium after 120 h of growth. Scale bar, 5 mm. (C) Colony biofilm surface area quantitation for the indicated strains after 120 h of growth. Error bars represent standard deviation of three independent experiments. (D) Colony biofilm height quantitation for the indicated strains after 120 h of growth. Error bars represent standard deviation of three independent experiments. (C and D) Only pairwise comparisons that had P value < 0.05 are denoted. Statistical significance was determined using Welch’s ANOVA with Dunnett’s T3 multiple comparisons test in GraphPad Prism software. ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05.