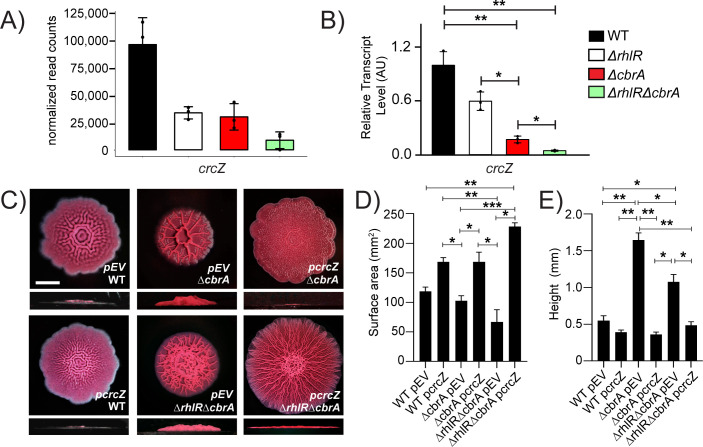
Fig 5.
CrcZ small RNA allows integration of Rhl- and Cbr-signaling pathways and modulates biofilm development. (A) Normalized read counts obtained via Median Ratio Normalization (MRN) analysis for crcZ gene from RNA-seq run on biofilm samples of WT and indicated mutants. (B) Relative expression of crcZ gene normalized to 16S RNA, ostA, and rpsO transcript levels measured by qRT-PCR in WT PA14 and indicated mutants after 120 h of colony biofilm growth. AU denotes arbitrary units. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates. (C) Colony biofilm phenotypes of WT PA14 and the designated mutants on Congo red agar medium after 120 h of growth. Scale bar, 5 mm. (D) Colony biofilm surface area quantitation for the indicated strains after 120 h of growth. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent experiments. (E) Colony biofilm height quantitation for the indicated strains after 120 h of growth. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent experiments. (B, D, E) Only pairwise comparisons that had P value < 0.05 are denoted. Statistical significance was determined using Welch’s ANOVA with Dunnett’s T3 multiple comparisons test in GraphPad Prism software. ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05.