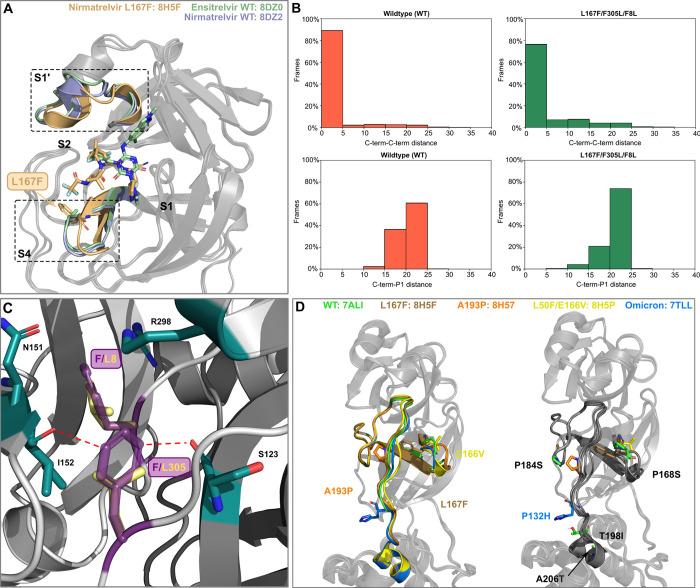
Fig 5. Structural analysis of mutants.
(A) Superposition of nirmatrelvir-WT (8DZ2), ensitrelvir-WT (8DZ0 [51]) and nirmatrelvir-L167F bound (8H5F [55]) crystal structures. L167F is colored in light brown and the two L167F-affected catalytic subpockets are highlighted with dotted-boxes (B) Bar plots showing the percentage of frames against C-term/C-term distance or C-term/P1 distance for WT (left) and for the L167F/F305L/F8L mutant (right). (C) The F8 and F305 aromatic side chains (dark violet) form a π-π T-stack and F8 in addition interacts with N151, I152, and R298 (green sticks, PDB entry 7ALI [56]). F8 is located within the homodimer interface. The conjugated p-orbitals of the F305 side chain are located nearby of the I152 and S123 backbone oxygen atoms, potentially leading to electronic repulsion. In the F305L mutant, the distance of the leucine side chain (yellow sticks) to these oxygen atoms is considerably increased. (D) Superposition of recent Mpro and Omicron crystal structures harboring different mutations (A193P (PDB entry: 8H57 [55]), or near (E166V (PDB entry: 8H5P [55]), L167F (PDB entry: 8H5F [55]) in the domain II-III linker loop, and the Omicron signature mutation (P132H (PDB entry: 7TLL [57]) (left panel). All residues that were found to alter the inhibitor binding and are also located on the domain II-III linker (T198I) or nearby (P168S, P184S and A206T) are mapped onto the structure in the right panel.