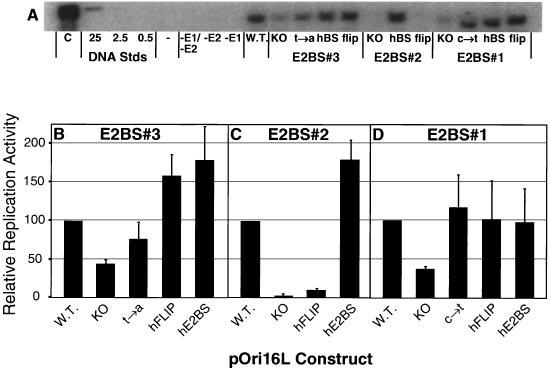
FIG. 8.
Transient-replication assays with pOri16L mutants. (A) Representative Southern blot prepared by electrophoresis of Hirt DNA digested with both AlwNI and DpnI, transferred to a nylon membrane, and visualized with radiolabeled probe made using pOri16L as the template. In the left lane is one-eighth of the wild-type sample that was digested only with AlwNI. The next three lanes contain dilutions of DNA standards (in picograms) to control for hybridization efficiency between blots. (Because all cells are not efficiently transfected by the electroporation procedure, these standards cannot be used to determine pOri16L copy numbers replicated per cell) The lanes labeled −E1/−E2, −E2, and −E1 were transfected with wild-type (W.T.) pOri16L alone or with the addition of only the E1 or E2 expression plasmid respectively. The remaining lanes are labeled with the name of the pOri16L clone (3 μg) that was transfected into SCC-13 cells along with the E1 and E2 expression plasmids (in equal molar amounts; 3 μg of pOri16L plus 3.3 μg of pCMV-E216 plus 3.8 μg of pCMV-E116). Southern blots were exposed to PhosphorImager screens and analyzed using ImageQuant software. Shown are the relative replication activities from three independent transfections of pOri16L templates with mutations to their (B) E2BS#3, (C) E2BS#2, or (D) E2BS#1. Error bars correspond to the standard deviation for each data set.