Figure 1.
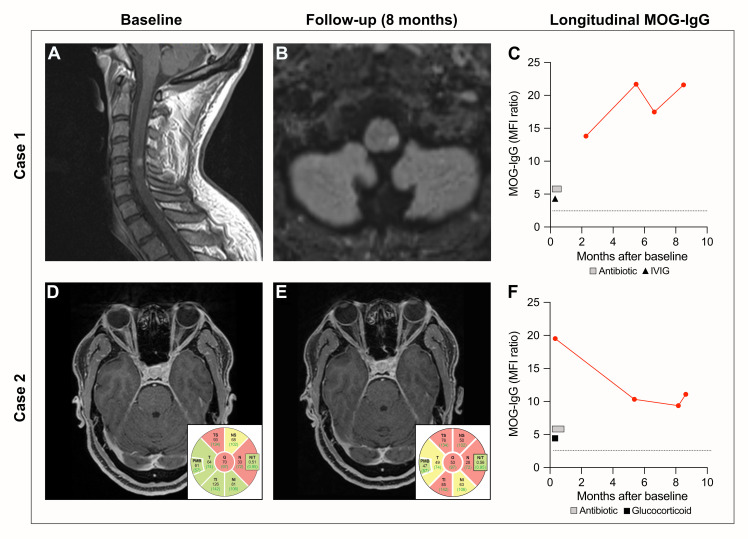
Clinical features at baseline and follow-up. Case 1: (A) Spinal MRI with sagittal T1 showing contrast-enhancing lesion on the level of cervical vertebrae 4/5, presenting as numbness in the genital area and both legs. (B) Cerebral MRI with transversal FLAIR revealing a new lesion in the left brainstem 6 months after initial treatment with IVIG. (C) Longitudinal MOG-IgG values (geometric MFI ratio). The dotted line indicates the cutoff for clear-positive MOG-IgG signals (geometric MFI ratio = 3). The square indicates treatment with an antibiotic (intravenous penicillin [20 million units/day] for 14 days) and the triangle indicates IVIG treatment (150 g over 5 days). Case 2: (D) Transversal T1 showing contrast enhancement of the right optic nerve at diagnosis. OCT showing slightly (yellow) and severely (red) diminished pRNFL thickness of the right eye. (E) Transversal post-contrast T1 showing bilateral normal optic nerves; however, OCT showed a decrease of the pRNFL thickness of the right eye 8 months after initial treatment with methylprednisolone. (F) MOG-IgG values (geometric MFI ratio) at baseline and follow-up time points. Cutoff for clear-positive MOG-IgG signals (geometric MFI ratio = 3) indicated as a dotted line. The square indicates treatment with an antibiotic (benzathine penicillin [2.4 million U/week] over 3 weeks) and the triangle indicates treatment with glucocorticoids (methylprednisolone 3 g over 3 days). MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; FLAIR, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; IVIG, intravenous immunoglobulin; MOG, myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; OCT, optical coherence tomography; pRNFL, peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer.