Fig. 8.
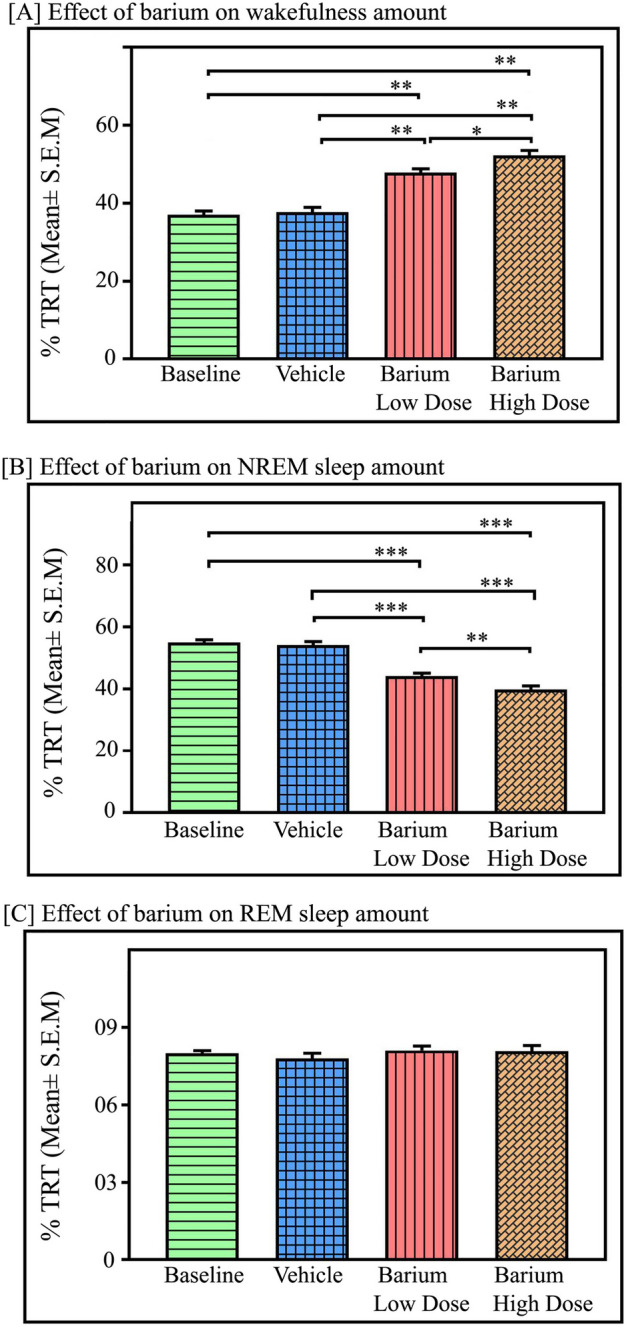
Effects of Kir channel inhibition in the RTN on sleep–wake architecture. Microinjections of kir channel blocker BaCl2 in the RTN (n = 6) significantly increased (A) wakefulness amount compared to the baseline and vehicle p < 0.01, F(3,23) = 78.85), One way RM ANOVA, followed by post-hoc Tukey test. (B) However, BaCl2 microinjections with low dose (1 mM) and high dose (2 mM) in the RTN significantly decreased NREM sleep amount compared to baseline and vehicle (p < 0.001, F(3,23) = 88.61). (C) However, REM sleep amount did not change either with a low dose or a high dose of BaCl2 microinjections into the RTN compared to baseline or vehicle (p > 0.05; F(3,23) = 40.39). *Denotes p < 0.05, ** denotes p < 0.01, *** denotes p < 0.001.
