Table 2.
Characterization of actinic keratosis by reflectance confocal microscopy and evaluation methods.
| Attribute | Example and grading | What to observe |
|---|---|---|
| 1—Hyperkeratosis |
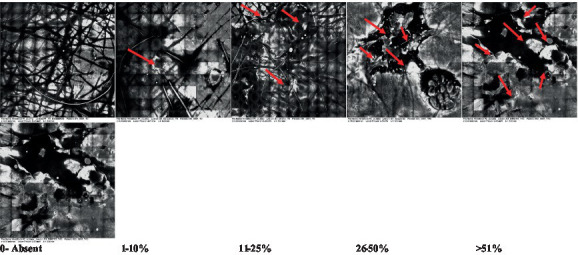
|
Presence and spreading of visible refractory and amorphous structures in the stratum corneum and augmented thickness of the layer |
| 2—Parakeratosis |
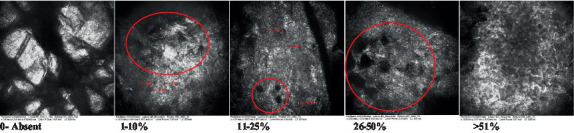
|
Presence and percentage of spreading area of visible nucleated polygonal cells in the stratum corneum |
| 3—Desquamation of the stratum corneum and corneocyte cohesion |
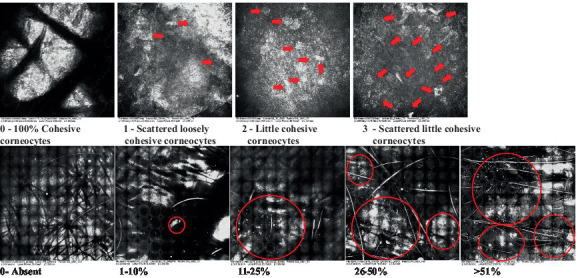
|
Different levels of cohesiveness of corneocytes and presence and spread of loose horny plates, “chunks” of scattered corneocyte clusters |
| 4—Cellular atypia in the viable epidermis |
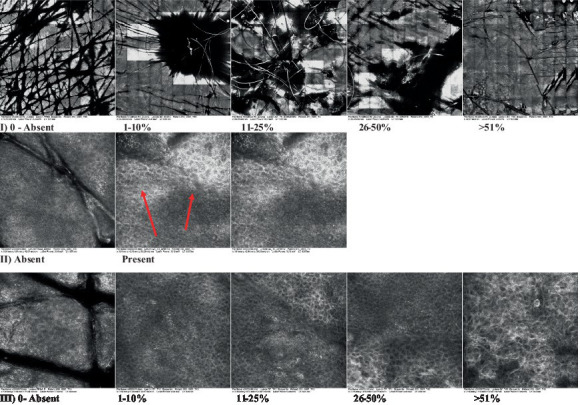
|
Presence and level of disorder in the shape of the cluster of cells of the viable epidermis (I—atypical honeycomb pattern), stratum espinosum (II—disarrangement) and granulosum (III—atypical honeycomb pattern), respectively |
| 5—Dyskeratosis |
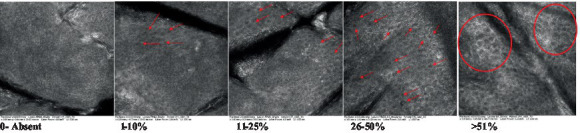
|
Presence and spreading of rounded nucleated cells in the stratum espinosum |
| 6—Inflammatory (dendritic) cells in the epidermis |
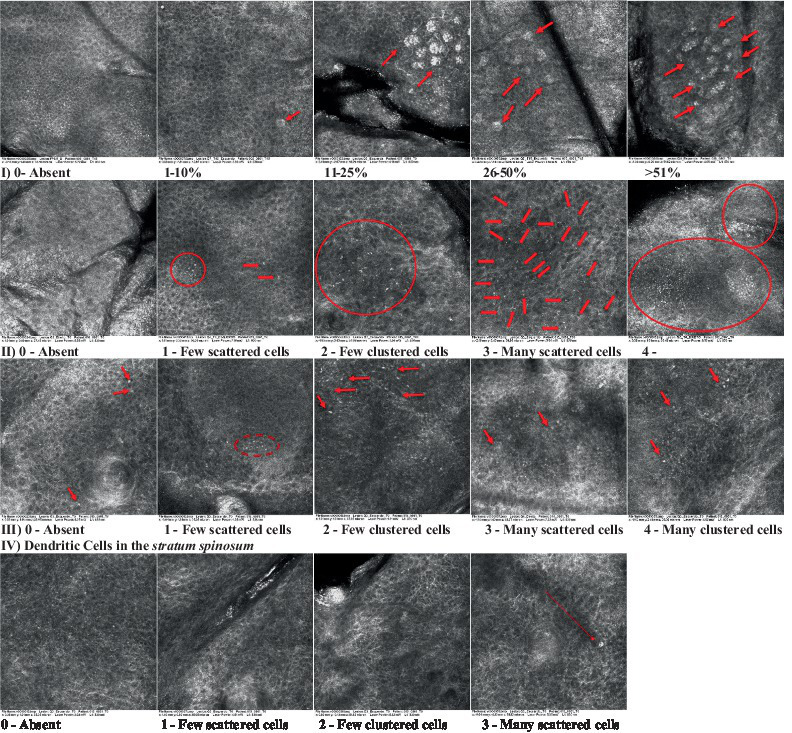
|
Presence and spreading of rounded and refractile cells, appearing in small groups in the stratum granulosum (I—lymphocytes, and II—rounded dendritic cells) and espinosum (III—lymphocytes and IV—dendritic Cells), respectively |
| 7—Nuclear pleomorphism in the stratum spinosum |
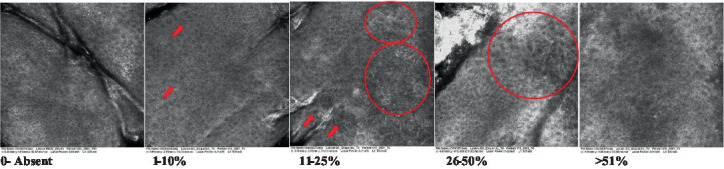
|
Variations in the size and shape of cells and nuclei in the stratum spinosum |
| 8—Atypical keratinocytes with follicular coverage |
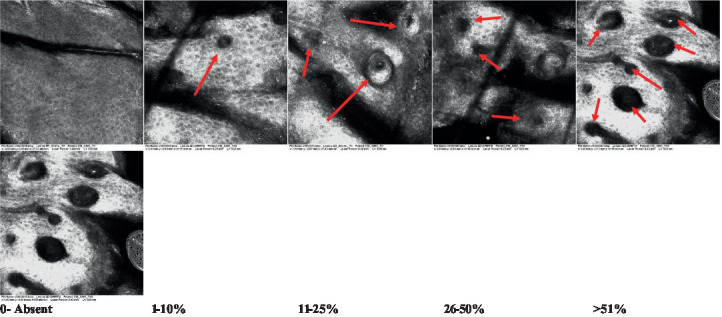
|
Presence and spreading of dark openings with great refraction of surrounding cells |
| 9—Poorly defined boundaries between keratinocytes |
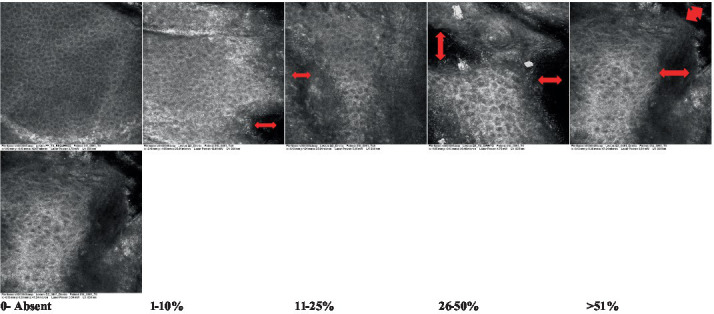
|
Presence and spreading of Irregular connections between keratinocytes |
| 10—Inflammatory cells in the basal layer |
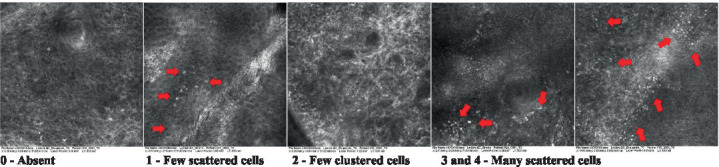
|
Presence and spreading of small and scattered refractable cells in the basal layer |
| 11—Cellular apoptosis in the viable epidermis |
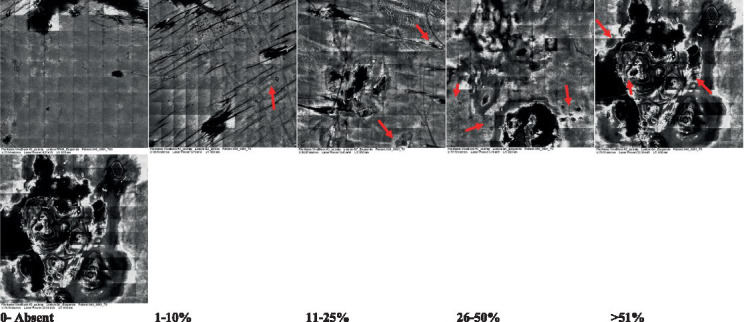
|
Presence and spreading cell death in spots of the epidermis, darkened cytoplasm and bright nucleus |
| 12—Fibers around the dermal papillae |
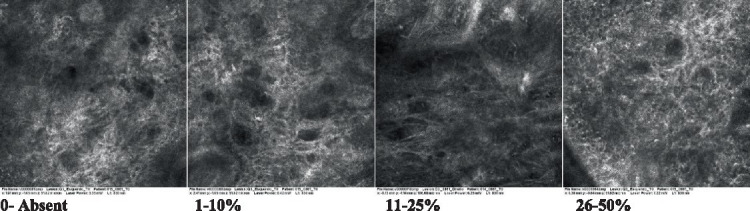
|
Presence and spreading of entangled fibers and dense material around the papillae. Poorly defined papillae |
| 13—Papillary irregularity |
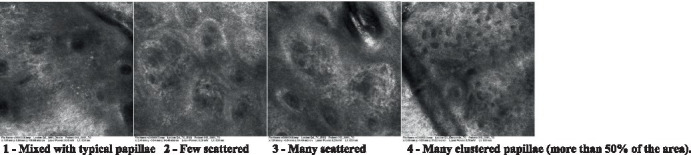
|
Presence and spreading of poorly defined dermal papillae surrounded by dense material |
| 14—Rounding of blood vessels in the papillary dermis |
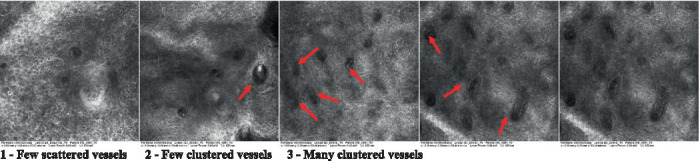
|
Presence of rounded blood vessels traversing the papillae. Refractive cells = blood cells |
| 15—Melanocytes clustered in the dermis |
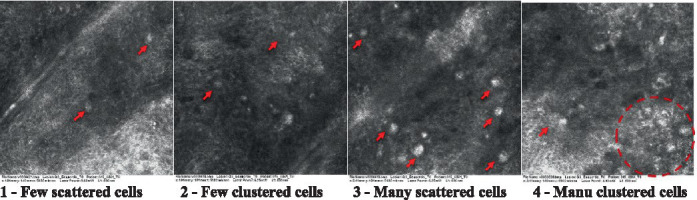
|
Presence and spreading of bulky melanocytes |
| 16—Solar elastosis |
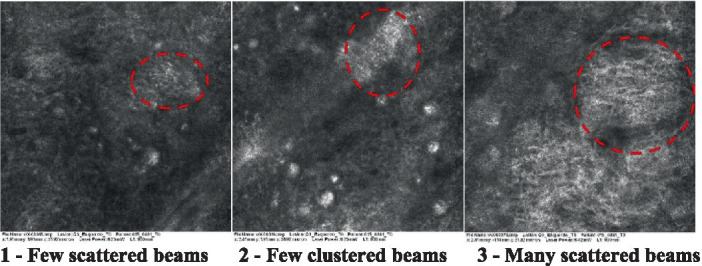
|
Presence of degraded elastic and collagen fibers in the skin |
| 17—Brain-like, finger-like appearances |
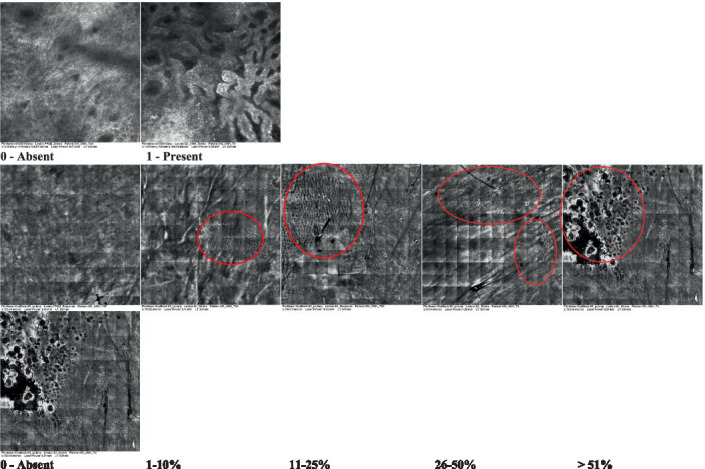
|
Presence and spreading of clusters of rounded, misshapen cells |
| 18—Dermal nests |
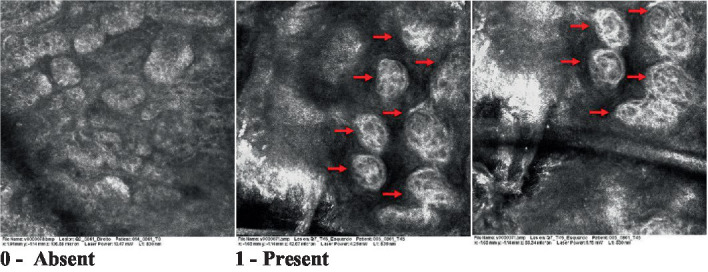
|
Presence of cell clusters in the dermis |
Observations: the presence/absence of each attribute was observed and the relative proportion of the injured area to the total area of the block was calculated. The percentage was then established: 0 for absence; 1–10%; 11–25%; 26–50% and above 50%. Arrows point to individual structures and circles highlight larger regions containing structures. The photos that do not present any highlighted structure are considered the general perspective of the structures present throughout the image.
