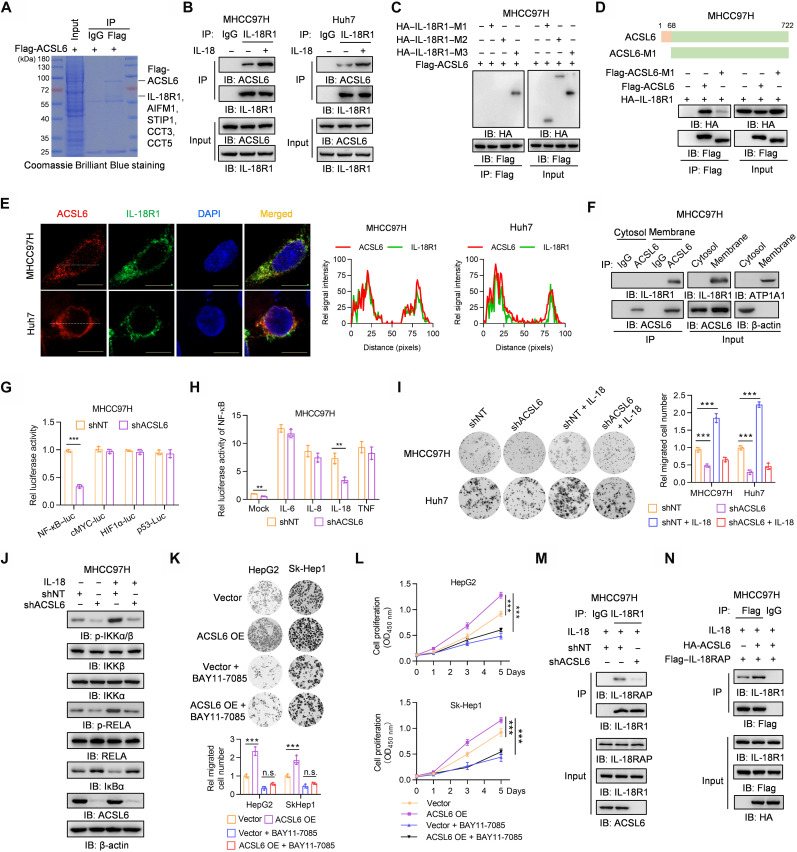
Fig. 3. ACSL6 activates the IL-18–IL-18R1–NF-κB pathway by forming a complex with IL-18R1.
(A) Flag-ACSL6 was immunoprecipitated from MHCC97H cells expressing Flag-ACSL6, and then SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) followed by Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining and mass spectrometry (MS) analysis was performed. (B) MHCC97H and Huh7 cells were treated with or without IL-18 (20 ng ml−1) for 1 hour. (C) MHCC97H cells expressing Flag-ACSL6 were transfected with hemagglutinin (HA)–tagged vector, IL-18R1–M1, IL-18R1–M2, or IL-18R1–M3. (D) MHCC97H cells expressing HA–IL-18R1 were transfected with vector, Flag-ACSL6 WT, or M1. (E) Immunofluorescence (IF) analyses of ACSL6 and IL-18R1 colocalization in MHCC97H and Huh7 cells. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. (F) Membrane and cytosol fractions were prepared from MHCC97H cells. (G) Luciferase analyses in shNT and shACSL6 MHCC97H cells. HIF1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1α. (H) Luciferase analyses of NF-κB–luc in shNT and shACSL6 MHCC97H cells treated with IL-6, IL-8, IL-18, and TNF (20 ng ml−1) for 12 hours. (I) Transwell assays in shNT or shACSL6 MHCC97H and Huh7 cells treated with or without IL-18 (20 ng ml−1). (J) Immunoblotting analyses in shNT and shACSL6 MHCC97H cells treated with or without IL-18 (20 ng ml−1) for 1 hour. (K and L) Transwell (K) and CCK-8 assays (L) in vector or ACSL6-overexpressed (OE) HepG2 and Sk-Hep1 cells treated with or without 10 μM BAY11-7085. n.s., not significant. (M) MHCC97H cells expressing shNT or shACSL6 were treated with IL-18 (20 ng ml−1) for 1 hour. (N) MHCC97H cells expressing Flag–IL-18RAP were infected with HA-ACSL6 and then treated with IL-18 (20 ng ml−1) for 1 hour. [(B) to (D), (F), (M), and (N)] Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting analyses were performed with indicated antibodies. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. Student’s t test [(G) and (H)], one-way ANOVA [(I) and (K)], and two-way ANOVA (L).