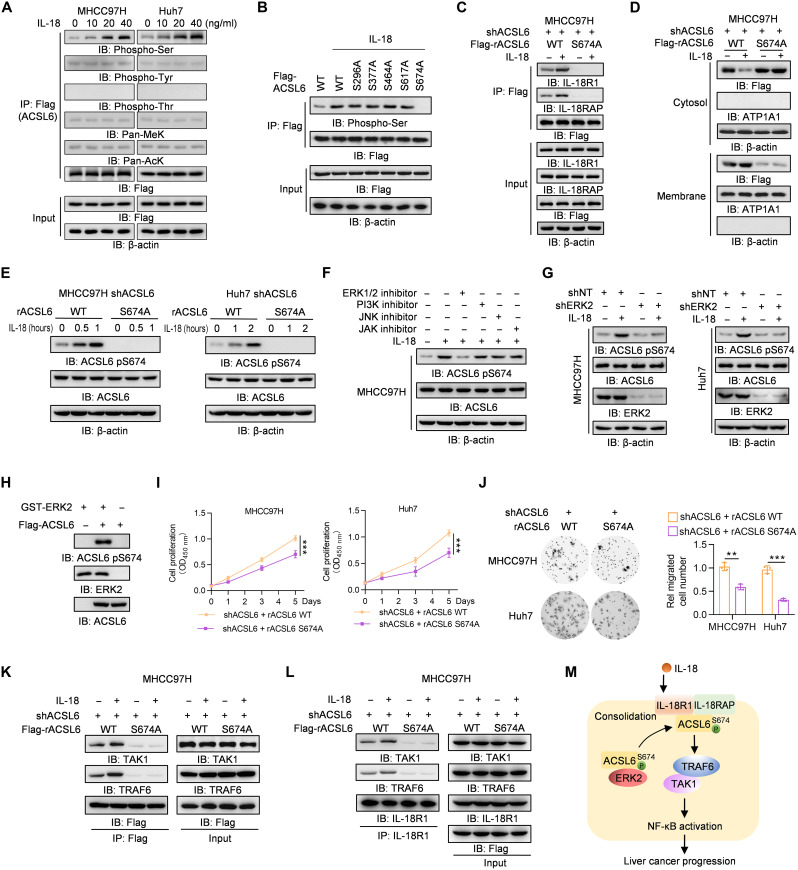
Fig. 4. IL-18 induces ACSL6 pS674 to activate NF-κB signaling.
(A) Flag-ACSL6–overexpressed MHCC97H and Huh7 cells were treated with different concentrations of IL-18 for 1 hour. Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting analyses were performed. (B) Flag-ACSL6 WT and mutant overexpressed cells were treated with or without IL-18 (20 ng ml−1) for 1 hour. Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting were performed. (C and D) ACSL6-depleted MHCC97H cells were infected with Flag-ACSL6 WT or S674A and then treated with or without IL-18 (20 ng ml−1) for 1 hour. Immunoprecipitation (C) and subcellular fractionation detection (D) were performed. (E) Immunoblotting analyses in ACSL6-depleted MHCC97H and Huh7 cells reconstituted with Flag-rACSL6 WT or S674A and treated with or without IL-18 (20 ng ml−1) for indicated times. (F) Immunoblotting analyses in MHCC97H cells treated with or without indicated inhibitors for 6 hours, followed by treatment with IL-18 (20 ng ml−1) for 1 hour. (G) Immunoblotting analyses in shNT or shERK2 MHCC97H and Huh7 cells treated with or without IL-18 (20 ng ml−1) for 1 hour. (H) In vitro kinase assay was performed by mixing GST-ERK2 and Flag-ACSL6. (I and J) CCK-8 (I) and transwell assays (J) in ACSL6-depleted MHCC97H and Huh7 cells reconstituted with rACSL6 WT or S674A. (K and L) ACSL6-depleted MHCC97H cells were infected with Flag-rACSL6 WT or S674A and then treated with or without IL-18 (20 ng ml−1) for 1 hour. Immunoprecipitation analyses were performed using anti-Flag (K) or anti–IL-18R1 antibodies (L). (M) Mechanism through which ACSL6 activates the IL-18–IL-18R1–NF-κB pathway by forming a complex with IL-18R1 and consolidating the IL-18R1–IL-18RAP heterodimer. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. Two-way ANOVA (I) and one-way ANOVA (J).