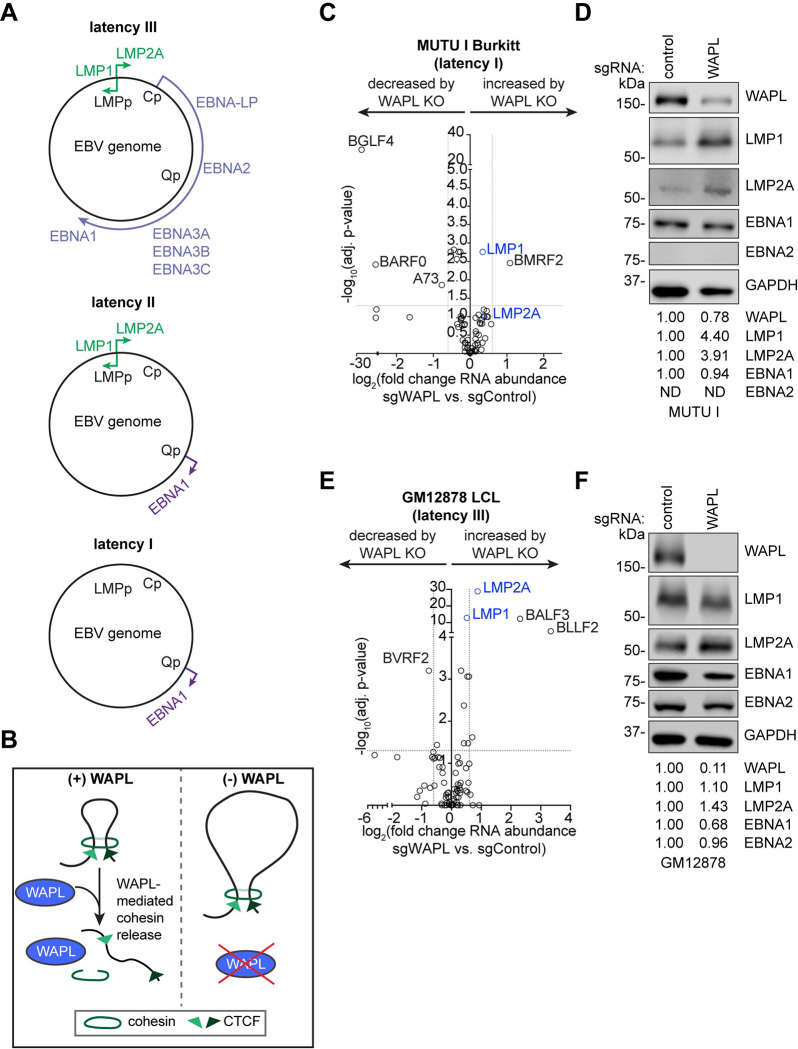
Fig 1. WAPL negatively regulates LMP1 and LMP2A expression.
(A) Schematic diagram of EBV latency programs. (B) Schematic of WAPL antagonism of cohesin-mediated DNA loop formation. WAPL releases cohesin to promote dissolution of chromatin loops. Upon WAPL KO, cohesin occupancy on chromatin increases, resulting in larger DNA loops. (C, E) Volcano plots of RNA-seq analysis visualizing -log10(adj. p-value) vs. log2(fold change of EBV mRNA abundance) from (C) Cas9+ MUTU I Burkitt lymphoma cells and (E) Cas9+ GM12878 LCLs expressing WAPL vs. control sgRNAs, from n = 3 independent biological replicates. (D, F) Immunoblot analysis of whole cell lysates (WCL) from (D) MUTU I cells and (F) GM12878 LCLs expressing control or WAPL sgRNAs, as indicated, representative of n = 3 biological replicates. Shown below are densitometry values that were normalized to GAPDH loading control, with control levels normalized to 1. ND indicates not detected.