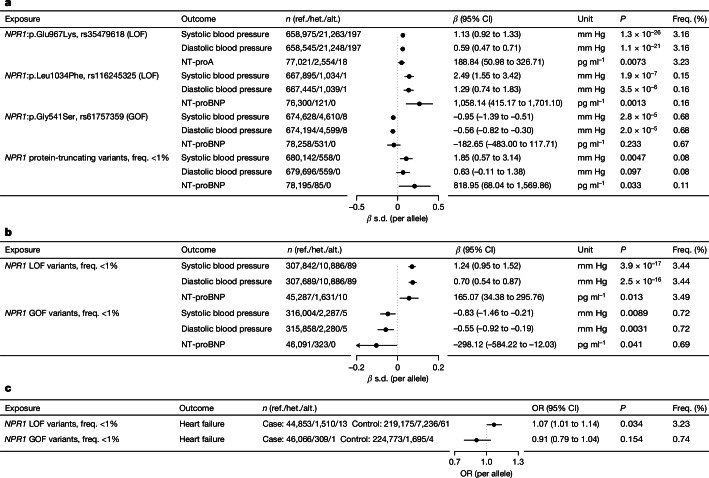
Fig. 1. Protein-altering genetic variants in NPR1 and the associated effect on BP and NT-proBNP in 718,386 individuals.
a, We replicated three previously reported and functionally validated missense variants with a known effect on BP15. Two reported LOF variants (NPR1:p.L1034F-rs116245325 and NPR1:p.G967K-rs35479618) were associated with increased BP and higher NT-proBNP, while a reported GOF variant (NPR1:p.G541S-rs61757359) was associated with lower BP and directionally lower NT-proBNP. We also found that individuals carrying a protein-truncating variant (presumed LOF) of NPR1 on average have higher BP and higher NT-proBNP than that of non-carriers. b, We defined any protein-altering variant associated with increased BP as presumed LOF (n = 9) and any BP-decreasing protein-altering variant as presumed GOF (n = 5). In an independent sample, we found that the combined collection of presumed LOF variants is associated with increased BP and higher NT-proBNP, while the collection of presumed GOF variants is associated with decreased BP and lower NT-proBNP. c, The collection of presumed LOF variants is associated with increased odds of HF, while the collection of presumed GOF variants is numerically associated with a decreased odds of HF, based on an additive genetic model performed in independent samples. Alt., alternative allele; CI, confidence intervals; freq., frequency; het., heterozygous allele; OR, odd ratio; ref., reference allele.