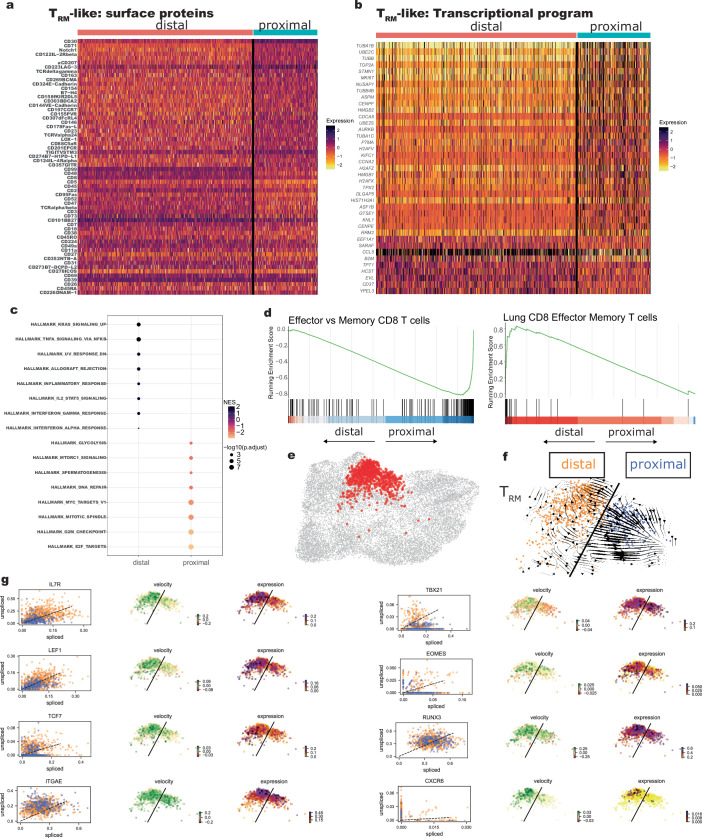
Extended Data Fig. 10. Surface proteomic and transcriptional asymmetry between first-division proximal-daughter and distal-daughter TRM-like CD8 CARTs.
a-b, Heat map of (a) normalized surface protein levels of the top 30 proteins enriched in either distal-daughters or proximal-daughters and (b) normalized gene expression of top enriched genes in either distal-daughters or proximal-daughters demonstrate asymmetry in surface proteome and transcriptional abundance between first-division proximal-daughter and distal-daughter TRM-like CARTs. c, Hallmark transcriptional programs of distal and proximal TRM-like CARTs support interferon alpha and gamma response in distal-daughters and increase metabolic activity (glycolysis, MTORC1 signaling) and proliferation (MYC targets, mitotic spindle, G2M checkpoint, E2F targets) in proximal-daughters. Statistical significance was determined using GSEA test with Benjamini–Hochberg correction for multiple comparisons. d, Gene-set enrichment plot between distal and proximal TRM-like CARTs demonstrate enrichment of lung effector memory cell-associated programs in distal-daughters and effector cell-associated programs in proximal-daughters. e, Proximal and distal TRM clusters (clusters TRM21 and TRM10) characterized in f-g. f, Velocity vector projection onto TRM UMAP clusters with streamline plots indicating divergent cell-state transitions between proximal-daughters and distal-daughters. Black line signifies border between distal (orange) and proximal (blue) cells. g, Gene-specific RNA velocity displayed as spliced/unspliced transcripts (left column) and projected onto TRM UMAP clusters (middle column), with normalized gene expression levels as a comparison (right column) demonstrating intrinsic upregulation of IL7R, LEF1, TCF7, and CXCR6 in distal-daughters compared to proximal-daughters. Plots are representative of 2 independent experiments with distinct donors: one with the anti-TCRδ CAR (shown in this figure) and one with the anti-CD19 CAR.