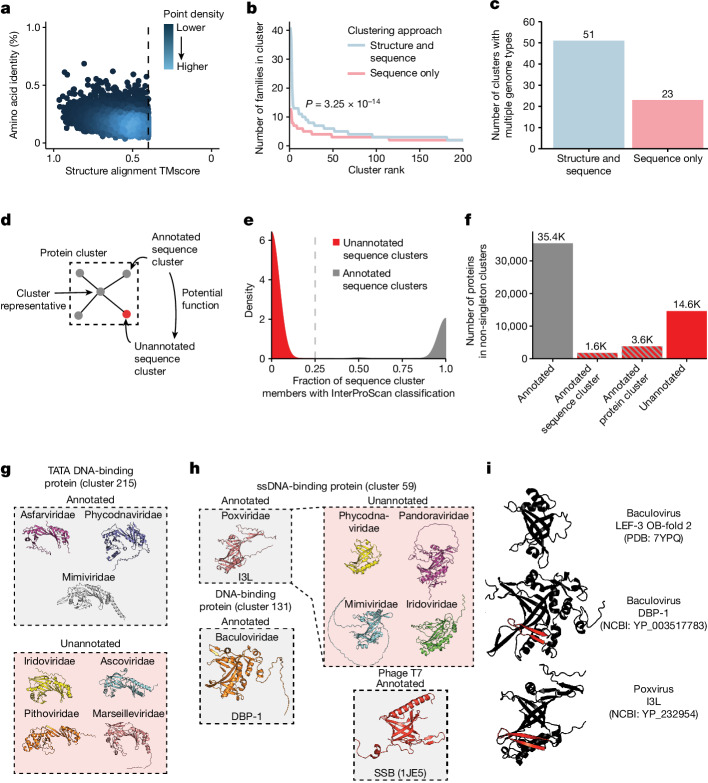
Fig. 2. Structural alignments link annotated and unannotated sequence clusters.
a, Structure and sequence similarity between protein cluster representatives. Each dot indicates a single alignment. b, Viral family diversity in clusters generated by structure and sequence or sequence alone. The top 200 clusters by number of members were plotted. The P value is from a two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test. c, The number of clusters that contain proteins from viruses with different genome types when using structure and sequence or sequence only. d, Structural similarity between InterProScan annotated and unannotated protein clusters has the potential to provide functional information. e, The percentage of sequence cluster members with an InterProScan classification is plotted against the density of sequence clusters with each percentage. Sequence clusters with fewer than 25% of members having InterProScan classifications were considered unannotated sequence clusters. f, Counts of proteins annotated by InterProScan or in a protein or sequence cluster with a protein annotated by InterProScan. g, Cluster 215 contains TATA DNA-binding proteins. NCBI Protein accessions: YP_009703143, YP_008052367, YP_003969792, YP_009021140, YP_009701471, YP_009000953 and YP_009094710. h, Cluster 59 contains a widespread family of ssDNA-binding proteins. NCBI Protein accessions: YP_232954, NP_048769, YP_008437003, YP_003970005, YP_009272775 and YP_003517783. These folds share an oligonucleotide fold with phage T7 single-stranded binding protein. i, I3L-like eukaryotic ssDNA-binding proteins contain a distinct N-terminal beta sheet that is absent in other OB-folds such as those present in baculovirus LEF-3.