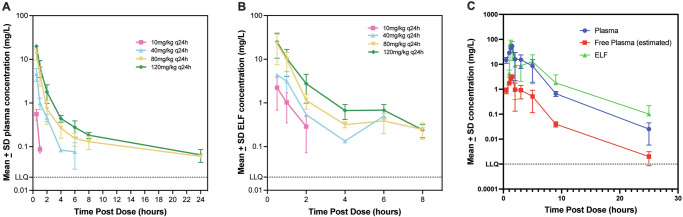
Fig. 3. Determination of pharmacokinetics (PK) in the plasma and epithelial lining fluid (ELF) in neutropenic mice and rats following infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
A In neutropenic CD-1 mice, (n = 3/cage, per dose for each time point) thigh infection model, plasma PK was determined following subcutaneous administration of 10, 40, 80 and 120 mg/kg of BWC0977 q24h following infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa NCTC 13921 and plasma samples taken at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 24 h post-dosing (n = 3/cage, per dose for each time point). Data plotted as mean ± SD. (B) The ELF was obtained by instilling 2 ml of sterile saline into the lungs of mice and removing saline from the lungs twice at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8 h post-dosing. Plasma protein binding was estimated to be ~87%. Data plotted as mean ± SD. C In the neutropenic rat (n = 3) lung infection model, 100 mg/kg of BWC0977 was administered following infection with P. aeruginosa ATCC27853. The ELF and plasma samples were taken at 0.5, 1 h (during infusion), and post-infusion at 1.25, 1.5, 2, 3, 5, 9, 25 h post-dosing (n = 3, per dose for each time point). The ELF was obtained by instilling 2 ml of sterile saline into the lungs and removing saline from the lungs. The free plasma levels were calculated from the total plasma levels using the plasma protein binding value of 94%. For all evaluations mean per dose/time point ± SD is plotted.