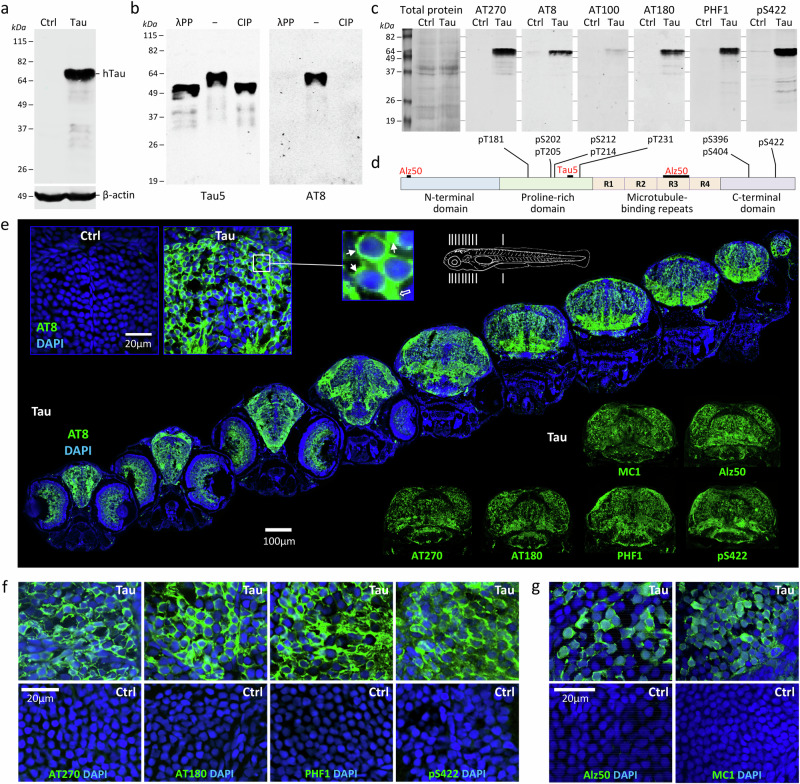
Fig. 3. Human 4R/0N-Tau hyperphosphorylation, mislocalization and misfolding throughout the CNS of transgenic Tau zebrafish.
a, b Western blots of zebrafish head region lysates at 3dpf. a Samples from Ctrl and Tau zebrafish, blot probed with antibodies to total human Tau and β-Actin. b Lysates from Tau zebrafish were pretreated with calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (CIP), Lambda protein phosphatase (λPP), or no enzyme (−). The blot was probed with an antibody to total human Tau (left) and an antibody to human phosphorylated [pS202, pT205]-Tau (AT8; right). c Replicate western blots of lysates from Ctrl and Tau zebrafish were probed with a panel of antibodies specific to different phosphorylated human Tau epitopes. The total protein loading control is shown for the first blot (left; others identical). d Major domains of human 4R/0N-Tau are shown to illustrate the locations of epitopes detected by the antibodies used in this study. e Serial axial sections (planes indicated in schematic at top) through a Tau zebrafish at 5dpf labeled for human phosphorylated Tau (AT8; green) and a nuclear counter label (DAPI; blue). The inset panels top left show similar sections from Ctrl and Tau zebrafish at higher magnification; the expanded panel illustrates mislocalization of human phospho-Tau to the cell bodies of neurons (small arrows) in addition to physiological localization in axons (large outline arrow). The inset panels below right show sections labeled with antibodies to other human Tau phosphoepitopes and misfolding epitopes as indicated. f, g Confocal micrographs showing sections from Tau (upper row) and Ctrl (lower row) zebrafish brain at 5dpf, labeled with antibodies recognizing (f) phosphorylated human Tau (AT270, AT180, PHF1 and pS422; green) or (g) misfolded human Tau (Alz50 and MC1; green), and a nuclear counter label (DAPI; blue). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.