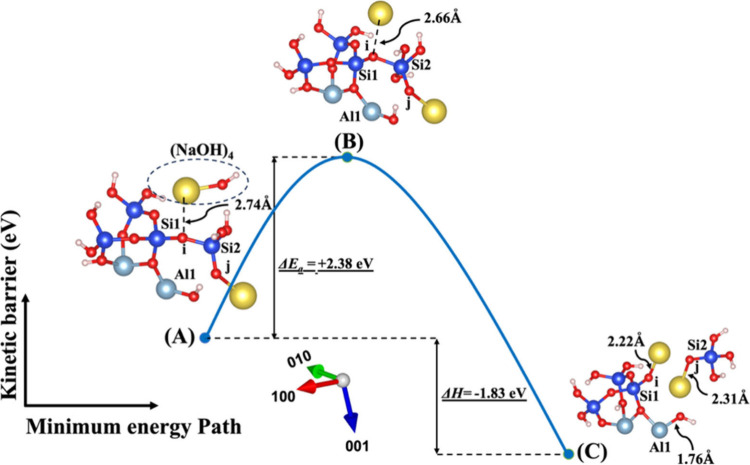
Figure 8.
Model 4. (A) The optimized geometric structure of the reactant, including (NaOH)4 molecules as the absorbent on the MK surface (001̅) obtained from model 2C (Figure 4) with the contribution of vdW interactions (Table S1) for breaking of the bridging oxygen (i) bonded to the silicate neighbor (Si2). (B) The transition state was identified at the saddle point using the improved dimer method. (C) The optimized geometric structure of the product after full saturation of the bridging oxygens (i, j) with two sodium cations (ionic bond) bonded to the silicate neighbors (Si1, Si2). The energy barrier (activation energy) of the hydrolysis reaction (ΔEa) and the energy change of reaction enthalpy (ΔH) obtained from first-principles calculations.