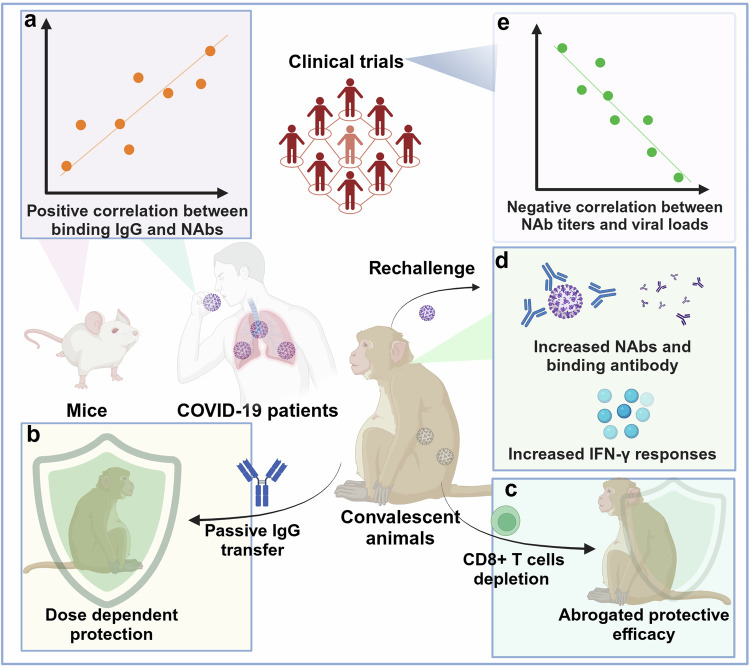
Fig. 3.
The determination of immune correlates in animal models and immune correlates in COVID-19 patients are taken as examples. a In animal models and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients, a positive correlation between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was confirmed. b, c In COVID-19 convalescent animals, passive transfer of serum IgG protects naïve animals in a dose-dependent manner, while CD8+ T-cell depletion abolishes this protective effect to some extent. d SARS-CoV-2 rechallenge in convalescent animals increased neutralizing antibody (NAb), virus-specific binding antibody and IFN-γ responses. e In large-scale human clinical trials, a negative correlation between NAb titers and viral loads was noted. Taken together, these findings suggest that NAbs and virus-specific IgG are responsible for improved protection against COVID-19, while cellular immunity partially contributes to this protection. (Created in BioRender)