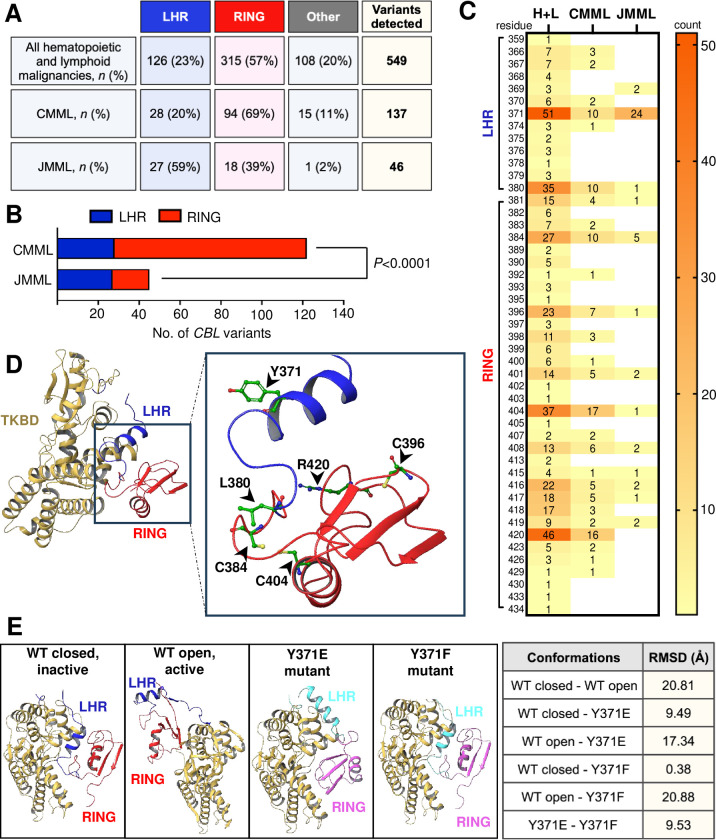
Fig 4. CBL mutation hotspots in CMML cluster in the RING domain, unlike in JMML where they more commonly occur within the LHR.
(A) Table of CBL variants detected in our PREACH-M cohort combined with data sourced from COSMIC. Variants include nonsense or missense substitutions, frameshift and in-frame insertions or deletions within the coding sequence of CBL, filtered for all hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies including CMML and JMML (n = 549), and CMML only (n = 137) or JMML only (n = 46) (B) Contingency analysis of CBL mutation hotspots within the LHR and RING domain of Cbl in CMML and JMML (C) Heat map representation of all sites within the LHR (amino acid residues 353–380) and RING domain (amino acid residues 381–435) where mutations have been reported. Numbers within the figure and on the scale depict counts (D) Tertiary protein structure of native wildtype Cbl (PDB ID 2Y1M) in inactive, closed conformation. The TKBD is colored beige, LHR blue and RING domain red. Amino acid residues of the top 6 mutation hotspots are indicated in inset; Tyrosine 371 (Y371), Leucine 380 (L380), Cysteine 384 (C384), Cysteine 396 (C396), Cysteine 404 (C404) and Arginine 420 (R420). (E) X-ray structures of wildtype Cbl in unphosphorylated, inactive state and in closed conformation (PDB ID 2Y1M), wildtype Cbl in Y371 phosphorylated, active state and in open conformation (PDB ID 4A4C), mutant Cbl Y371E (PDB ID 5HKX) and mutant Cbl Y371F (PDB ID 5J3X). The TKBD is colored beige, LHR of wildtype blue, LHR of mutant cyan, RING domain of wildtype red, RING domain of mutant pink. RMSD values between various Cbl conformations are shown in table. Statistical analysis was performed using two-sided Fisher’s exact test, where P<0.05 was statistically significant. [TKBD tyrosine kinase binding domain; LHR linker helix region; RING RING domain; H+L all hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies; WT wildtype; RMSD root mean square deviation (distanced-based measure of protein structure similarity)].