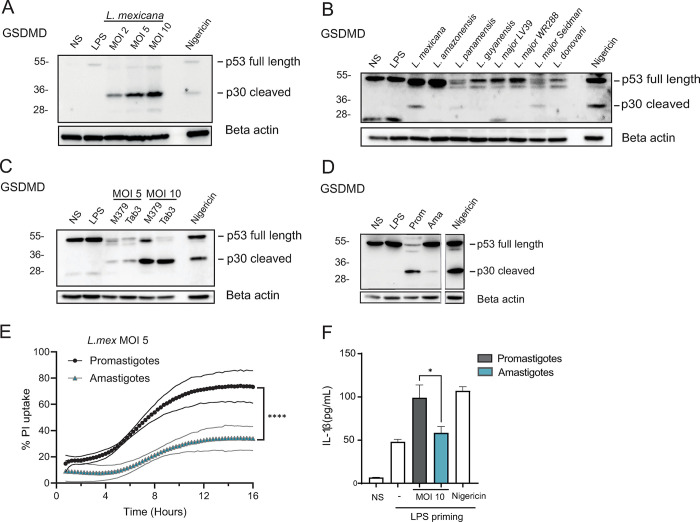
Fig 3. L. mexicana leads to inflammasome activation in neutrophils.
(A) Bone marrow-derived C57BL/6 neutrophils (BMNs) were isolated, primed with LPS and infected with L. mexicana promastigotes at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 2, 5, and 10 for 16 hours, or exposed to Nigericin for 4 hours as a positive control. Immunoblotting of GSDMD and beta-actin was performed on cell extracts. (B) BMNs were similarly infected with other Leishmania species at the MOI 5. (C) Comparison of GSDMD cleavage between L. mexicana M379 and Tab3 strains at the indicated MOI. (D) C57BL/6 BMNs were isolated, primed with LPS and infected at a MOI of 10 with L. mexicana promastigotes or axenic amastigotes, as indicated. Immunoblotting of GSDMD and beta-actin was performed on cell extracts and Nigericin was used as a positive control (same blot and exposure). (E) LPS-primed C57BL/6 BMNs were infected with L. mexicana promastigotes and axenic amastigotes at MOI of 5 and propidium iodide (PI) uptake was quantified over 18 hours of infection. (F) The corresponding IL-1β release in supernatants was assessed by ELISA. NS (non-stimulated), LPS (LPS 100ng/ mL priming alone), MOI (multiplicity of infection), Pro (promastigotes), Ama (amastigotes). Data are representative of >2 independent experiments. Differences between populations are analyzed by 2-way ANOVA (E) and Unpaired t-test (F).