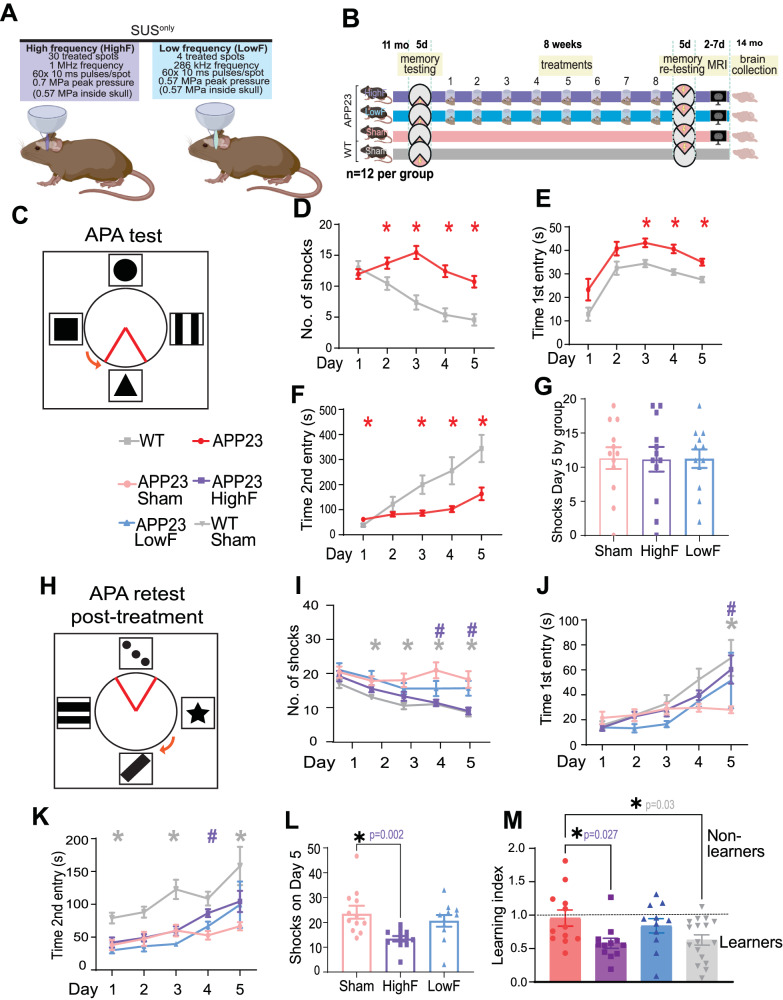
Fig. 1. Study design and spatial memory improvements in APP23 mice in response to SUSonly at 1 MHz (HighF).
A APP23 mice aged 11 months were treated with scanning ultrasound (SUSonly) at 1 MHz center frequency (HighF) or 286 kHz center frequency (LowF) with conditions arriving at the same pressure inside the skull, accounting for the higher attenuation of high frequency ultrasound. Exposure of the whole brain was achieved by treating a 5 × 6 grid of spots with the HighF device, and 4 spots with the LowF device, taking into account the different −6 dB widths of the ultrasound focus at HighF (1 MHz, 1.5 mm) versus LowF (286 kHz, 6 mm). B APP23 mice and wild-type (WT) littermate controls were tested in the active place avoidance (APA) test over 5 days of training. APP23 mice then received eight once-per-week ultrasound treatments with either the HighF or LowF device. Controls received a sham treatment consisting of anesthesia and being placed under the ultrasound transducer, but the transducer was not turned on. WT mice were sham treated. Three days after the last ultrasound treatment, mice were retested in the APA (retest) in which the extra-maze cues were changed, the shock zone was placed in the opposite quadrant, and the arena rotated in a different direction. Between 2 and 7 days after the conclusion of the APA, mice received magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans and were sacrificed at the conclusion of the scans. C Schematic of the arena for the APA test, in which mice must use spatial cues to learn to avoid a shock zone within a rotating arena. APP23 mice show impaired performance compared to their WT littermates on the measures (D) number of shocks, (E) time to first entry of the shock zone, and (F) time to second entry to the shock zone. (Two-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05, APP23 compared to WT). G All mice were ranked based on their performance on the last day (day 5) of the APA and allocated to groups based on matching performance. H Following eight ultrasound treatments (1 MHz ultrasound (HighF), 286 kHz ultrasound (LowF) or sham), the mice were retested in the APA with the shock zone location, extra-maze cues and the direction of the arena rotation altered. There were significant differences between the treatment groups, such that compared to sham treated APP23 mice, (I) HighF-ultrasound treated APP23 mice and sham treated WT mice received fewer shocks, (J) had an increased time to first entry on day five (K), and had an increased time to second entry of the shock zone. L HighF treated APP23 mice received significantly fewer shocks on day five of the APA retest compared to sham treated APP23 mice. (Two-way ANOVA with follow-up Holm–Sidak test, #p < 0.05 HighF compared to sham, *p < 0.05 WT compared to sham treated APP23 mice, #p < 0.05 HighF treated APP23 mice compared to sham treated APP23 mice). M A learning index was calculated by dividing the number of shocks received on day five compared to day one of the APA retest, with better learning indicated by a lower ratio on the learning index measure. HighF mice demonstrated better learning on this index (One-way ANOVA with Holm–Sidak multiple comparisons test, *p < 0.05).