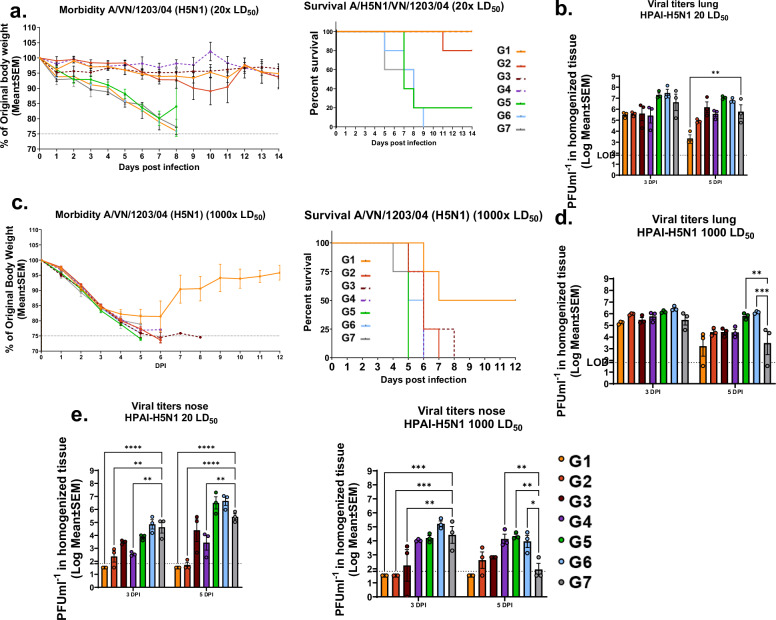
Fig. 10. cHA-LAIV vaccination protects mice from a high dose heterologous highly pathogenic avian influenza challenge and confers superior upper respiratory tract protection.
Foue weeks post final-boost, mice were challenged with an A/VN/1203/04/H5N1 virus using a lethal dose of 20x LD50.Thirteen weeks post final-boost the mice were challenged with high lethal dose 1000x LD50 challenge. a Morbidity (left) and mortality (right) were assessed by monitoring weight loss (20x LD50). b Viral titers in lungs (left) and nasal turbinates (right) on day 3 and 5 post-infection of challenged animals (20x LD50). c Morbidity (left) and mortality (right) were assessed by monitoring weight loss (1000x LD50). d Viral titers in lungs (left) and nasal turbinates (right) on day 3 and 5 post-infection of challenged animals (1000x LD50). Each dot represents one animal. Data is shown as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was compared to QIV-Standard of care group (Group 7) using one-way ANOVA using Dunnett’s-correction. ****P-<0.0001, ***P-0.0002, **P-0.0011, *P-0.02. Limits of detection (LOD) are shown in dotted lines.