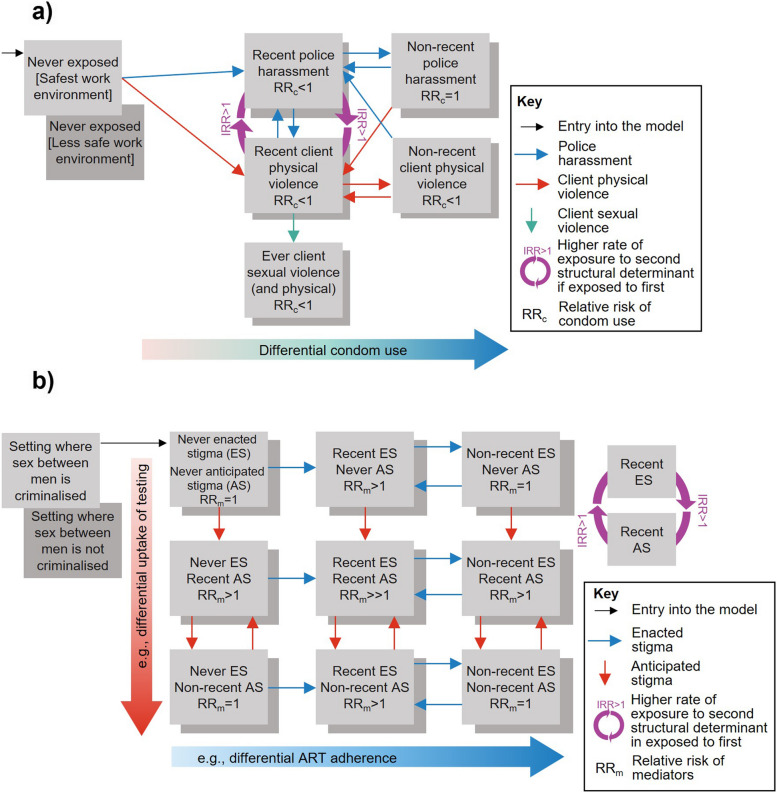
Fig. 2.
Dynamically representing exposure to structural determinants and their causal pathways in HIV models, with multiple different exposures and exposure histories. a Model flowchart (adapted from Shannon et al., 2015) [4] showing how exposure to different types of violence among FSW in different work environments and their impacts on HIV were represented in their model, and b a hypothetical model flowchart based on Shannon’s approach representing how exposure to stigma among MSM in settings could be modelled. Evidence suggests that in settings where sex between men is criminalised, MSM experience more stigma [59]. Enacted stigma, such as denial of care, and anticipated stigma, such as fear of discrimination, are linked to lower and slower uptake of HIV testing and treatment [60]. These could be represented by stratifying the population based on type of stigma, and criminalisation of sex between men, with multiple exposure histories for stigma to reflect short and long-term effects of exposure on HIV risks, and interactions reflecting links between the different exposures (purple arrow, incidence rate ratio for exposure; IRR > 1)