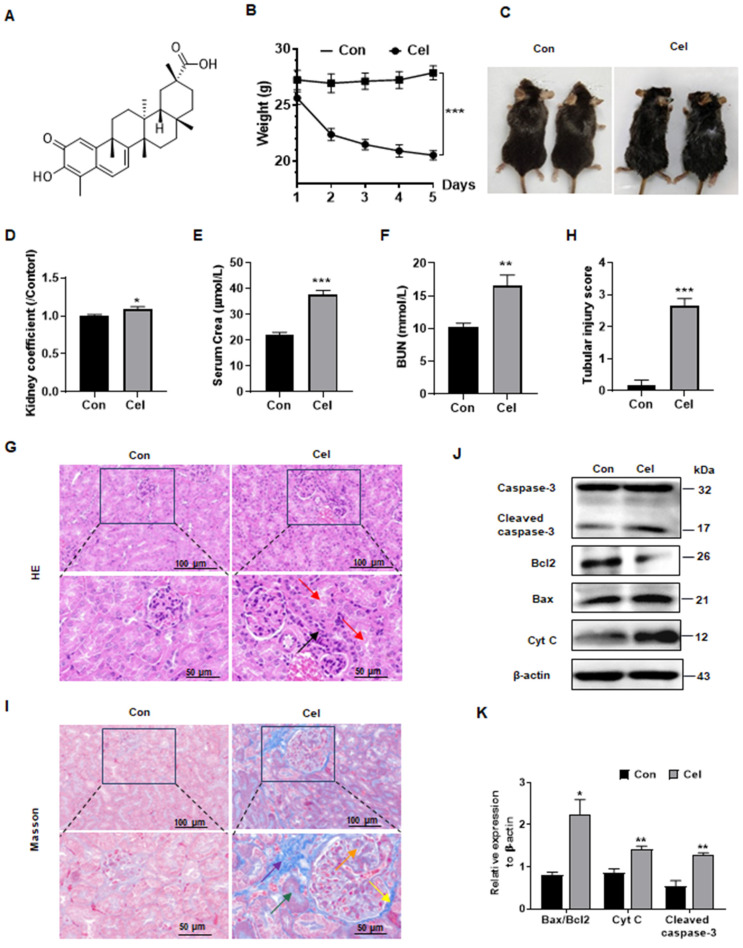
Figure 1.
Dysfunction and apoptosis of male mice kidney caused by Cel treatment. (A) Cel chemical structure. (B) Bodyweight reduction was caused by Cel (5 mg/kg/d, i.p.) in male C57 mice (n = 6, p < 0.001). (C) Mouse appearance. (D) Cel increased mouse kidney coefficient (n = 6, p = 0.04). Cel treatment caused kidney dysfunction in mice, resulting in a significant increase in serum Crea (E, n = 4, p < 0.001), BUN (F, n = 6, p = 0.005). (G) H&E staining, (H) tubular injury score (n = 6, p < 0.001) and (I) Masson trichrome staining of male mouse kidney tissue. Scale bar = 50, 100 μm. (J) Expression and (K) corresponding statistical result of the proteins related to apoptosis in male mouse kidney tissue upon Cel treatment according to WB. Data were analyzed using unpaired two-tailed t-test with Prism 8.2 (mean ± SEM). ns, no significance, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, vs. Control. Con, control, Cel celastrol, Crea creatinine, BUN blood urea nitrogen, H&E hematoxylin and eosin, WB western blotting, Cyt C cytochrome C, SEM standard error of the mean.