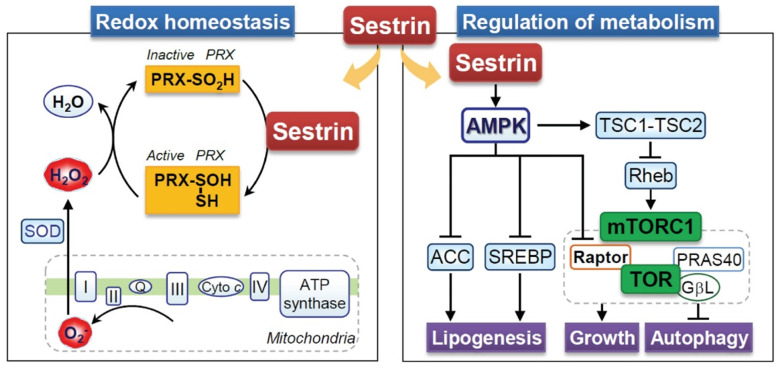
Figure 4.
Multifaced role of Sestrin in the regulation of metabolic and cellular redox homeostasis. Sestrin regulates cellular homeostasis over cellular growth, lipid synthesis (lipogenesis), and the vital process of autophagy, mainly by modulating the activity of the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) and its downstream targets. mTORC1 is a central regulator of cell growth and metabolism, and its dysregulation is implicated in various diseases. This Sestrin-mediated autophagy pathway regulates ROS levels and triggers redox adaptations under stress conditions. To maintain redox homeostasis, Sestrin stabilizes Nrf2 by inhibiting Keap1 and recycling peroxiredoxin (Prx), enhancing antioxidant defense. Activated (Prx) shows antioxidant activity by neutralizing H2O2 produced in mitochondria. ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase, SREBP: Sterol regulatory element binding protein, SOD: Superoxide dismutase, TSC: Tuberous sclerosis complex.