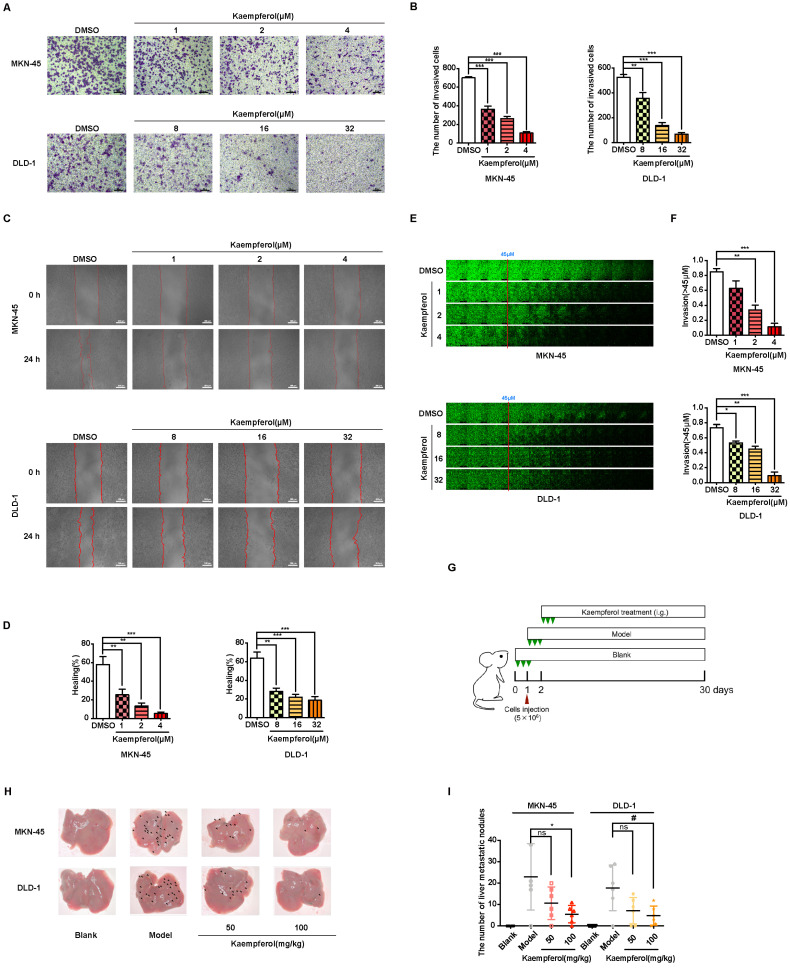
Figure 8.
Kaempferol inhibits gastrointestinal cancer metastasis both in vitro and in vivo. (A) Representative transwell assay images showing the migration of MKN-45 and DLD-1 cells treated with various concentrations of kaempferol. Random visual fields were selected for analysis. Scale bar: 500 μm. (B) Bar graphs showing the number of migrated MKN-45 and DLD-1 cells treated with different concentrations of kaempferol. Data are expressed as means ± SD, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (vs. DMSO group). (C) Representative wound healing assay images of MKN-45 and DLD-1 cells treated with different concentrations of kaempferol. (D) Healing rates of MKN-45 and DLD-1 cells treated with kaempferol at different concentrations. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (vs. DMSO group). (E) Inverted invasion assay evaluating the invasion capabilities of MKN-45 and DLD-1 cells in the presence of different concentrations of kaempferol. Scale bar: 250 μm. (F) Quantification of relative invasion of MKN-45 and DLD-1 cells over 45 μm (n = 3). Data are expressed as means ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (vs. DMSO group). (G) Schematic of the animal study: 5 × 106 MKN-45 or DLD-1 cells were injected into BALB/c nude mice, and 50 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg of kaempferol were administered intraperitoneally starting on day 2 post-injection (n = 8 per group). (H, I) Liver metastasis analysis in mice engrafted with MKN-45 or DLD-1 cells. Data are expressed as means ± SD, *P < 0.05 (vs. MKN-45 model group), #P < 0.05 (vs. DLD-1 model group).