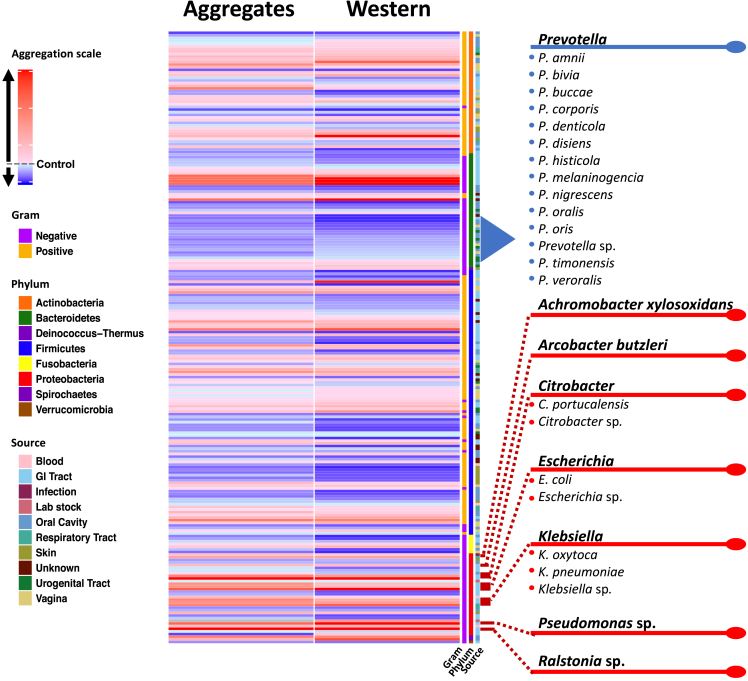
Figure 2.
Heatmap summarizing the results of the screen that assessed the effect of human bacterial isolates on C. elegans intestinal polyQ aggregation
PolyQ aggregation was quantified by microscopy (Aggregates column) and western blotting (Western column). Each of the 229 rows represents a single bacterial strain. Aggregation data are normalized to worms fed control E. coli OP50. The aggregation scale is color-coded from blue to red, where red indicates increasing polyQ aggregation relative to control. The characteristics (Gram, phylum, and source) of each bacterial isolate are included in the last three columns.