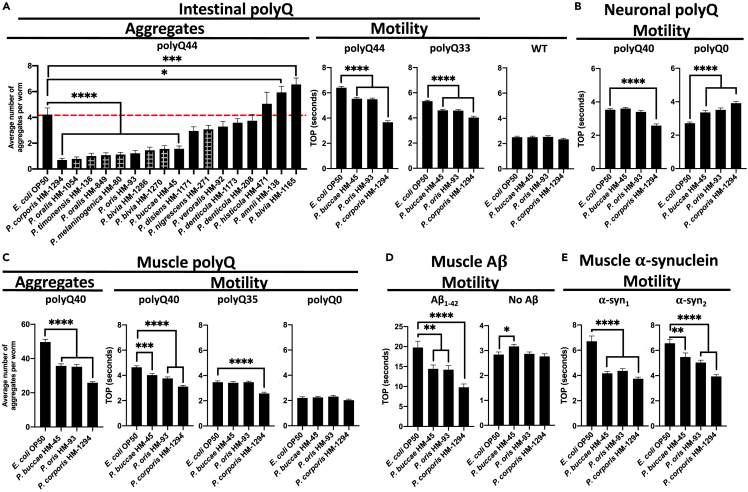
Figure 3.
The effect of Prevotella spp. on proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases
(A) The effect of Prevotella spp. on C. elegans intestinal polyQ aggregation (“Aggregates”) and the associated toxicity (“Motility”). Checkered bars represent bacteria-associated developmental delay. The three strongest suppressors of polyQ aggregation that did not affect development were tested using intestinal polyQ, (B) neuronal polyQ, (C) muscle polyQ, (D) muscle Aβ1-42, and (E) muscle α-synuclein. Data are represented as the average number of aggregates or TOP (seconds) per worm obtained from at least two independent experiments for a total of 30–60 worms. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA followed by multiple comparison Dunnett’s post-hoc test (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001).