Fig. 4.
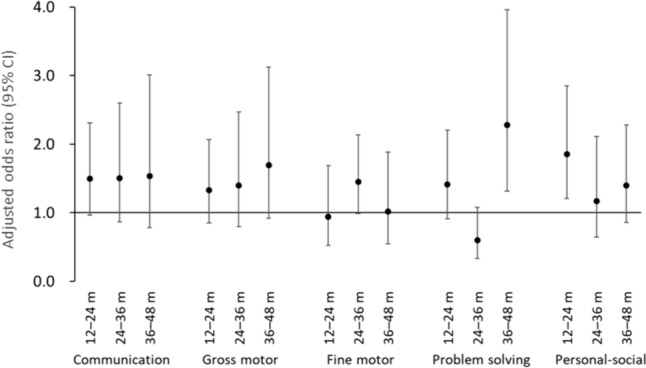
Association of general anesthesia before 1 year of age with the incidence of neurodevelopmental delay in children who did not receive general anesthesia during 1–4 years of age (n = 33,543). Adjusted odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the incidence of neurodevelopmental delay every 12 months after 1 year of age in each domain of the Japanese translation of the Ages and Stages Questionnaire (Third Edition) versus children who did not receive general anesthesia before 1 year of age. Adjusted for maternal age at delivery, body mass index before pregnancy, marital status, smoking status, early pregnancy occupational status, educational background, annual household income, fetal sex, gestational age at birth, use of any medication before and during pregnancy, mode of delivery, presence or absence of epidural analgesia, birth weight, presence or absence of nursery school attendance at 6 and 12 months of age, breastfeeding method during the first 6 months of life, and presence or absence of cohabiting siblings. A multiple imputation method was used to reduce potential selection bias from missing variables
