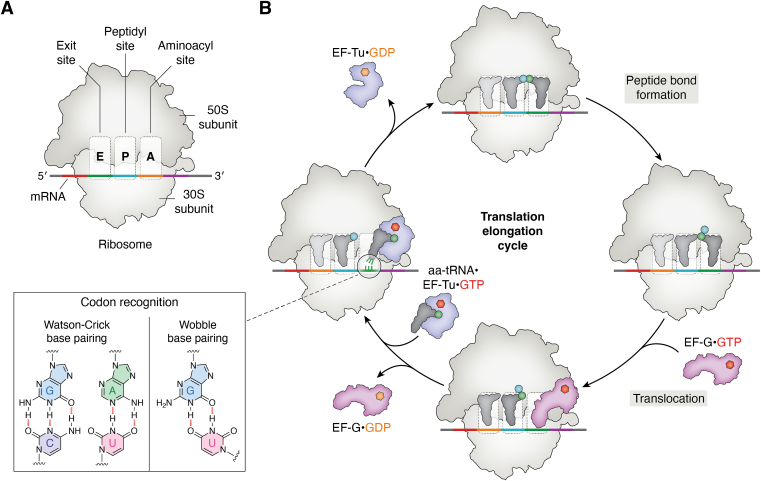
Figure 4.
Translation elongation cycle.A, the bacterial ribosome consists of a large (50S) and small (30S) subunit. tRNAs can bind three different cavities called the aminoacyl “A” site, peptidyl “P” site, and the exit “E” site. B, during translation elongation, aa-tRNAs are delivered as a complex with EF-Tu•GTP to the ribosome. mRNA codon recognition by the incoming tRNA-anticodon occurs via Watson-Crick base pairing and wobble-base pairing. After initial selection, the incoming aa-tRNA accommodates to the A-site, triggering EF-Tu GTP-hydrolysis, releasing it from the ribosome. Subsequently, the tRNA-bound A-site amino acid performs a nucleophilic attack on the tRNA-bound P-site amino acid, resulting in peptide bond formation. EF-G catalyzes the translocation of the mRNA-tRNA complex by one codon, which leaves the A-site idle to bind a new aa-tRNA.