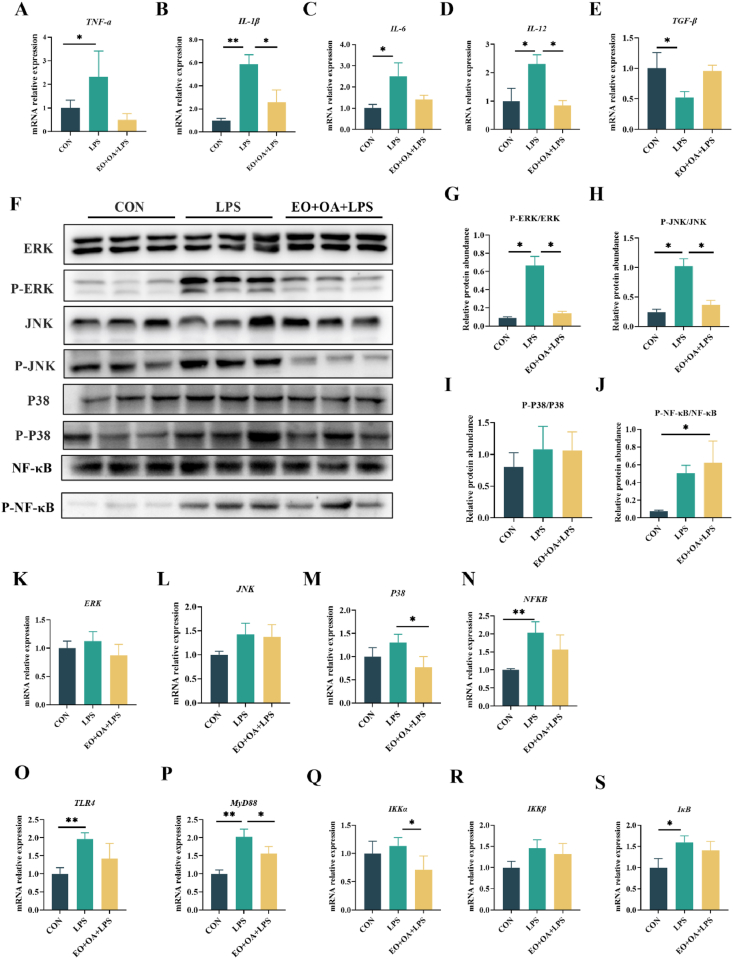
Fig. 5.
Effects of EO + OA on intestinal inflammation in weaned piglets. (A-E) Changes in intestinal inflammatory factors; (F-J) Western blotting was used to detect the protein levels of phosphorylated ERK (P-ERK), phosphorylated JNK (P-JNK), phosphorylated P38 (P-P38) and phosphorylated NF-ΚB (P-NF-ΚB) in the intestine (n = 3 replicates per group); (K-S) is a comparison of the mRNA relative levels of ERK, JNK, P38, NF-κB, TLR4, MyD88, IKKα, IKKβ and IκB (n = 6 replicates per group). CON = piglets fed the basal diet with intraperitoneal saline injection; LPS = piglets fed the basal diet and injected intraperitoneally with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to induce stress; EO + OA + LPS = piglets fed the basal diet supplemented with essential oils (EO) and organic acids (OA) and injected intraperitoneally with LPS to induce stress; JNK = c-Jun N-terminal kinase; ERK = extracellular regulated protein kinases; P38 = p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; IL-1β = interleukin-1 beta; IL-6 = interleukin-6; IL-12 = interleukin-12; TNF-α = tumor necrosis factor-α; TLR4 = Toll-like receptor 4; NF-κB = nuclear factor-kappa B; MyD88 = myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88; IKK = inhibitor of kappa B kinase; IκB = inhibitor of NF-κB. ∗ means significant difference (P < 0.05); ∗∗ means extremely significant difference (P < 0.01).