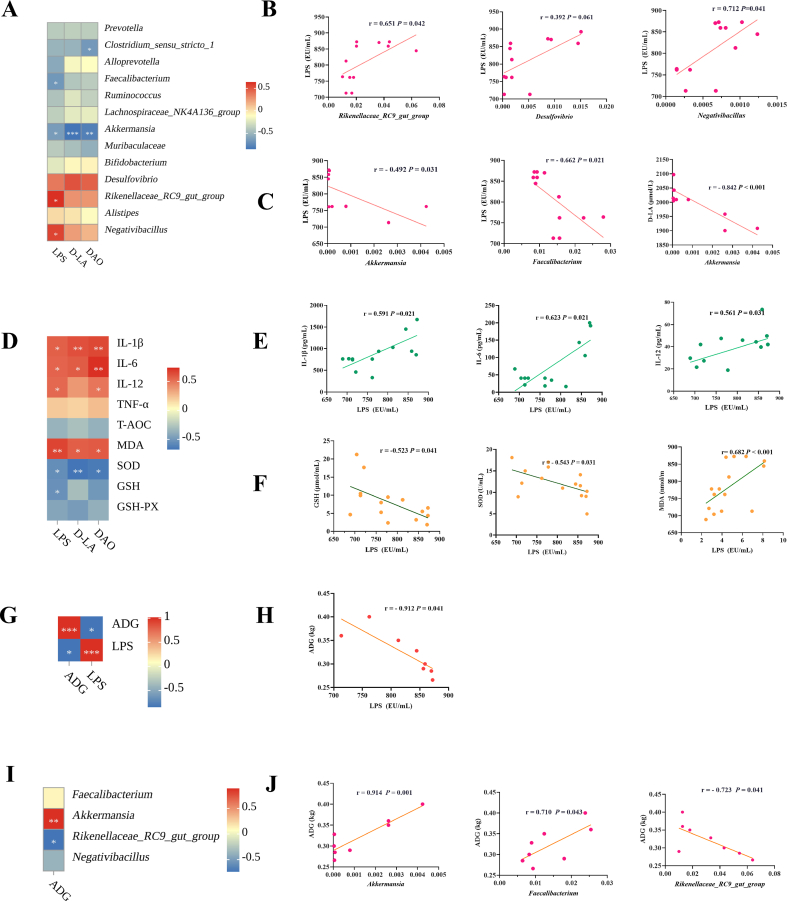
Fig. 8.
Correlation analysis between lipopolysaccharide (LPS) content and intestinal leakage indicators, intestinal inflammatory factors, and correlation analysis between plasma LPS content and intestinal microbiota. (A) Correlation of gut microbes with plasma LPS content and the gut barrier. (B) Linear correlation analysis with plasma LPS content for intestinal bacteria (Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_gorup, Desulfovibrio, Negativibacillus). (C) Linear correlation analysis with plasma LPS content for Faecalibacterium and Akkermansia, and linear correlation analysis with plasma D-LA content for intestinal bacteria Akkermansia, respectively. (D) Correlation analysis of plasma LPS content with plasma oxidative stress and plasma inflammation in the body. (E) Linear correlation analysis with plasma LPS content for plasma IL-β, IL-6 and IL-12 contents, respectively, in turn. (F) Linear correlation analysis with plasma LPS content for plasma MDA content, SOD activity, and GSH content, respectively, in turn. (G-H) Analysis of the correlation between plasma LPS content and piglet ADG. (I-J) Analysis of the correlation between intestinal microorganisms and the ADG of piglets. LPS = lipopolysaccharide; DAO = diamine oxidase; D-LA = D-lactic acid; TNF-α = tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL-1β = interleukin-1 beta; IL-6 = interleukin-6; IL-12 = interleukin-12; MDA = malondialdehyde; SOD = superoxide dismutase; GSH = reduced glutathione; GSH-Px = peroxisomal glutathione; ADG = average daily gain. ∗ means significant correlation (P<0.05), ∗∗ means very significant correlation (P<0.01), ∗∗∗ means extremely significant correlation (P<0.001).