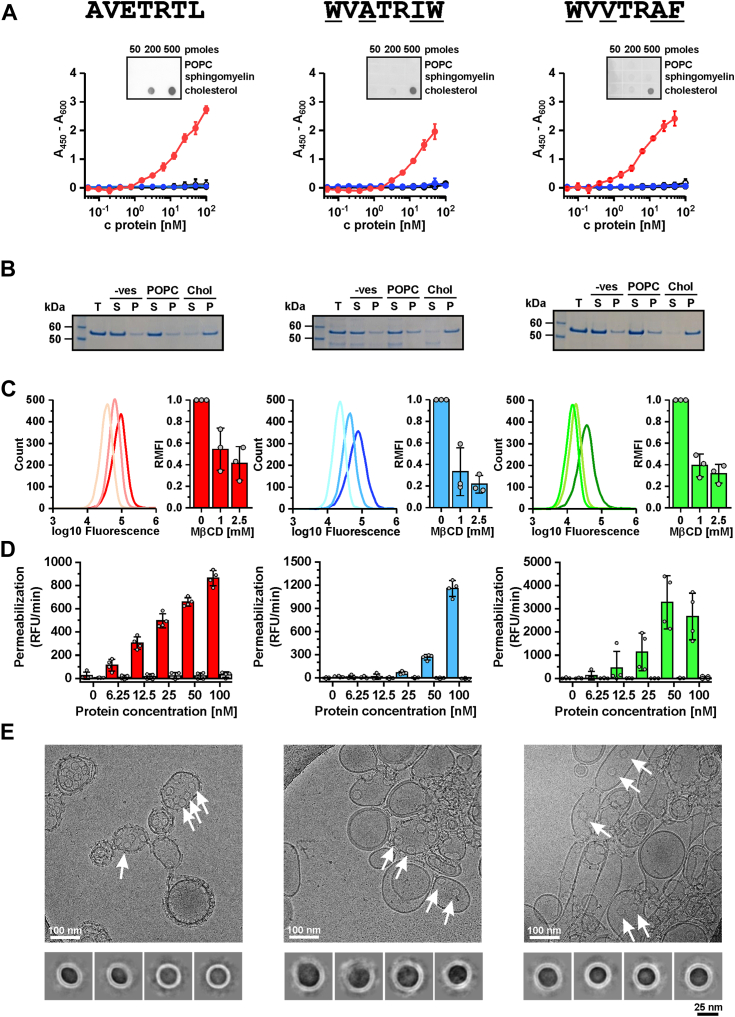
Figure 5.
Characterization of the cholesterol-specific functional and structural properties of the WVATRIW and WVVTRAF variants carrying alternative CRMs. The variants are named after the amino acids they contain at the positions studied by the combinatorial library. A, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The wells of the microtiter plates were coated with POPC (black), Chol (red), or cholesteryl-acetate (blue). The mean ± SD of three independent experiments is shown. The inset shows the results of lipid overlay assay where binding of the whole-length proteins to POPC, sphingomyelin, and cholesterol spotted to nitrocellulose membrane was analyzed. B, sedimentation assay of whole-length proteins with multilamellar vesicles composed of POPC or POPC with 50 mol% Chol (Chol). The vesicle-free sample (-ves) was used as a control. C, binding of EGFP-tagged D4 to the plasma membrane of RAW 264.7 cells in the absence or presence of methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβCD) at the indicated concentrations. The left panel for each protein shows flow cytometry data, and the graph on the right shows the green fluorescence of the cells (mean ± SD of three independent experiments). D, permeabilization of Raw 267.4 cells with whole-length WT PFO (red) and variants WVATRIW (blue) and WVVTRAF (green). Permeabilization is shown as the maximum rate of increase in fluorescence of the nuclear dye Sytox Green, which is not permeable to intact membranes. In each panel, responses in intact cells (the intense color) are compared to cells with MβCD-extracted Chol (pale color) (mean ± SD of four independent experiments). E, cryo transmission electron microscopy micrographs of whole-length WT and PFO variants bound to large unilamellar vesicles composed of POPC and 50 mol% Chol (top). Arrows indicate pores imaged as inserted rings. 2D class averages of top views of pores inserted in the vesicle lipid bilayer. Size bars (in nm) are depicted on micrographs and under the 2D class averages (right). P, pellet; RFU, relative fluorescence units; S, supernatant; T, total amount of protein used in the binding reaction.