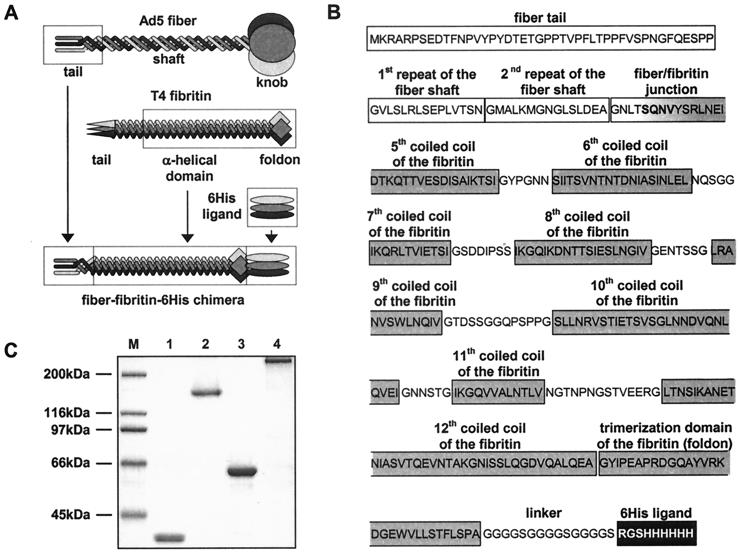
FIG. 1.
Generation of Ad5 fiber-T4 fibritin chimera containing targeting ligand. (A) Schema showing key components of the fiber-fibritin-ligand chimera and their sources. The tail of the fiber anchors the fiber–fibritin–six-His chimera in the Ad virion; a fragment of the fibritin protein provides trimerization of the molecule, while the six-His ligand mediates binding to an AR. (B) Amino acid sequence and domain structure of the FF/6H chimera. FF/6H protein is a 373-amino-acid-long molecule which consists of the amino-terminal segment of Ad5 fiber sequence genetically fused with the carboxy-terminal portion of the T4 fibritin protein, followed by the linker and the six-His-containing ligand. The beginning of the third pseudorepeat of the fiber shaft domain (GNTLSQNV) is joined to the fibritin sequence starting with the fragment of the insertion loop (SQN) preceding the fifth coiled-coil segment of the α-helical central domain of the fibritin (VYSRLNEIDTKQTTVESDISAIKTSI). The sequence SQNV present in the native structures of both fusion partners was chosen as the hinge between the two molecules in order to minimize potential structural conflicts between the β-spiral configuration of the fiber shaft and the triple α-helix of the central domain of the fibritin. The segments of the fibritin sequence localized between every two adjacent coiled coils are the insertion loops which provide some degree of flexibility needed for optimal ligand presentation. A peptide linker is incorporated between the carboxy-terminal trimerization domain (foldon) of the fibritin and the six-histidine-containing ligand to extend the ligand away from the carrier protein in order to facilitate binding to the target receptor. The domain organization of the fiber and the fibritin proteins is as published previously by Van Raaij et al. (30) and Tao et al. (27), respectively. (C) SDS-PAGE analysis of E. coli-expressed, immobilized metal ion chromatography-purified FF/6H chimeric protein. Lane M, molecular mass protein ladder; lanes 1 and 2, FF/6H protein; lanes 3 and 4, wild-type Ad5 fiber. The samples in lanes 1 and 3 were denatured by being boiled, which resulted in degradation of trimeric proteins to monomers, while lanes 2 and 4 contain proteins in their native trimeric configuration.