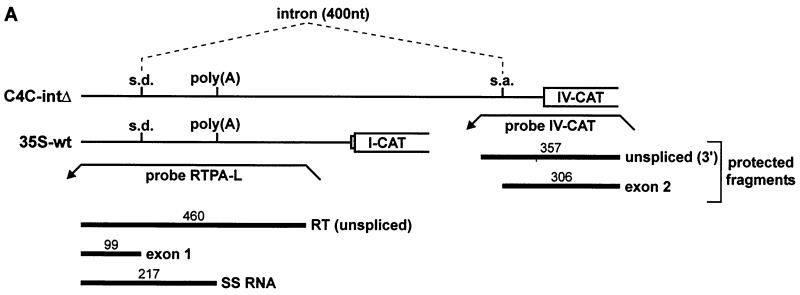
FIG. 6.
SS-RNA is unaffected by splicing of the viral intron. (A) Constructs C4C-intΔ and 35S-wt are depicted schematically, with the positions of the splice donor (s.d.), splice acceptor (s.a.), and poly(A) site indicated. Splicing of the 400-nt intron is indicated by dashed lines. Probes RTPA-L and IV-CAT are shown as leftward pointing arrows. The position and size (in nucleotides) of protected fragments are shown underneath. (B) Representative RNase protection analyses of the constructs shown in panel A, expressed in either rice (left panel) or N. plumbaginifolia (right panel) protoplasts. Probes RTPA-L and IV-CAT were used together in each sample. Protected fragments are labeled and named as in panel A. In rice protoplasts, some splicing events occurred on the 35S-wt transcript, presumably using cryptic acceptor sites within the CAT ORF or in the vector sequences. (C) The amount of SS-RNA in percent (calculated as SS/[SS+RT+exon 1]).