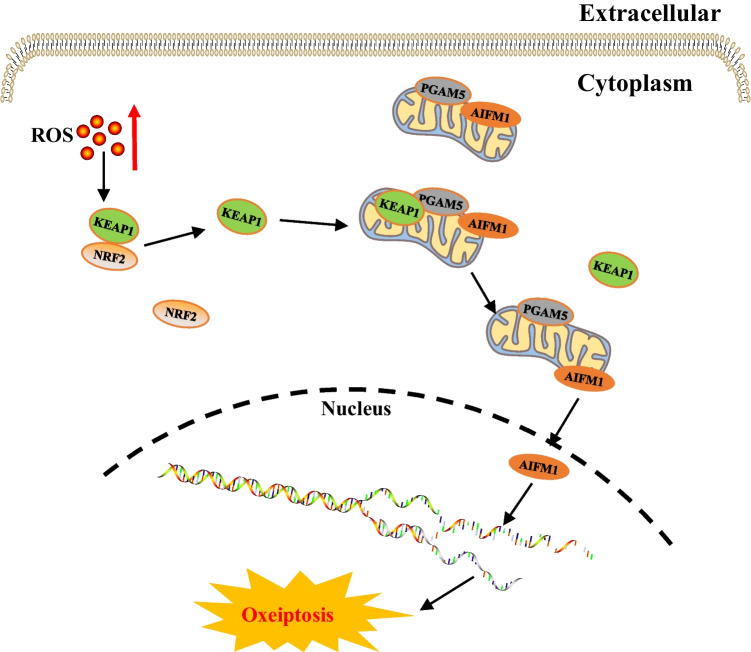
Fig. 3.
The core molecular mechanisms of oxeiptosis. High intracellular ROS levels induce conformational changes in KEAP1, triggering its dissociation from NRF2. KEAP1 translocates into mitochondria and mediates the release of AIFM1 from PGAM5 and AIFM1 translocation to the nucleus, where it dephosphorylates AIFM1 at S116, triggering cell death. Abbreviations: KEAP1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein-1; NRF2, Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; PGAM5, phosphoglycerate mutase family 5; AIFMI, apoptosis-inducing factor mitochondria associated 1