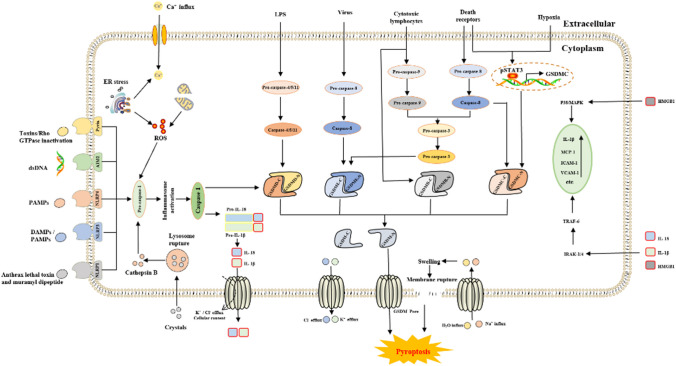
Fig. 9.
The core molecular mechanisms of pyroptosis. In response to DAMPs and PAMPs, cytosolic canonical inflammasomes (NLRP3, NLRP1, NLRC4, AIM2, pyrin, etc.) can respond to microbial infection (microbial toxins, etc.) or danger signals (dsDNA and crystals, etc.) to activate caspase-1, while noncanonical inflammasomes directly respond to LPS or other stimuli to activate caspase-4/5/11. After the activation of inflammatory caspases, pro-IL-1β, pro-IL-18, and GSDMD are cleaved to liberate N-terminal GSDMD (GSDMD-N), which forms pores on the plasma membrane and releases inflammatory mediators (IL-1β, IL-18, etc.). Other pathways involved in pyroptosis include the activation of caspase-3, caspase-8 and caspase-9 and the cleavage of gasdermin E, B and C (GSDME, GSDMB, and GSDMC, respectively). GSDMC is cleaved by caspase-8 and transcriptionally upregulated under hypoxic conditions through the interaction of pSTAT3 with programmed death-ligand 1. The amino-terminal PFD of gasdermin N then interacts with the plasma membrane, and 16 monomers oligomerize to form a gasdermin pore. The diameter of these pores is estimated to be in the range of 10–15 nm, which is large enough to release small proteins, including mature IL-1β (4.5 nm diameter), probably at a slow rate. Furthermore, sodium enters the cell, bringing water into the cell, which causes the cell volume to increase. This process can rapidly exceed the capacity of the membrane, resulting in membrane rupture. In response to membrane rupture, all the remaining soluble cytosolic contents are released so rapidly that it is essentially instantaneous, resulting in pyroptosis. Abbreviations: dsDNA, double-stranded DNA; PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; NLRP1/3/4, NLR family pyrin domain-containing 1/3/4; AIM2, absent in melanoma 2; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; GSDM B/C/D/E, gasdermin B/C/D/E; IRAK-1/4, interleukin receptor associated kinase 1/4; TRAF-6, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; ICAM-1, intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; pSTAT3, phospho-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3