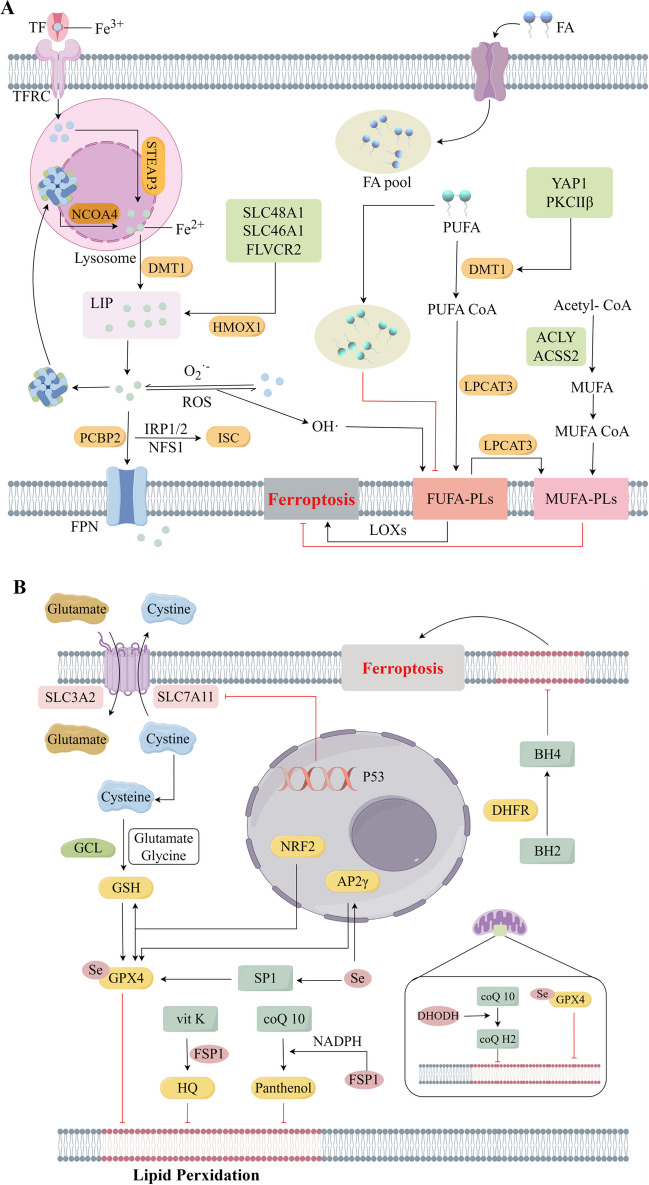
Fig. 1.
Regulatory mechanisms of ferroptosis. A. Intracellular iron metabolism and lipid metabolism synergistically induce ferroptosis. Fe3+ is transported intracellularly via TF and TFRC, and lysosomal digestion mediated by STEAP3 releases Fe2+ to replenish the LIP. Fe2+ undergoes the Fenton reaction, releasing large amounts of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and free radicals. Fatty acid uptake increases the intracellular pool of fatty acids. PUFA catalyzed by acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 (ACSL4) and LPCAT3 form PUFA-phospholipids (PLs), which are susceptible to oxidative stress and promote ferroptosis mediated by lipoxygenases (LOXs). An increase in monounsaturated fatty acid phospholipids (MUFA-PLs) as well as a decrease in polyunsaturated fatty acid phospholipids (PUFA-PLs) inhibits ferroptosis. B. The antioxidant pathway plays a crucial role in inhibiting intracellular ferroptosis. cystine/glutamate transporter (System Xc-) promotes intracellular cysteine uptake and induces the expression of GSH and GPX4, leading to increased antioxidant effects and inhibition of lipid peroxidation in cell membranes. NRF2, AP-2γ, and SP1 all upregulate the expression of GPX4, thereby enhancing the antioxidant effects. Additionally, FSP1 increases intracellular production of HQ and ubiquinol, exerting antioxidant effects. The promotion of BH4 synthesis by DHFR also results in antioxidant effects. Within mitochondria, both DHODH and GPX4 have the capability to inhibit ferroptosis by blocking lipid peroxidation. Abbreviations: ACLY, ATP citrate lyase; ACSS2, Acetyl-CoA synthetase 2; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; DHFR, dihydrofolate reductase; DHODH, dihydroorotate dehydrogenase; DMT1, divalent metal-ion transporter-1; FSP1, Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1; GCL, glutamate-cysteine ligase; GPX4, Glutathione Peroxidase 4; GSH, glutathione; HMOX1, heme oxygenase 1; HQ, hydroquinone; IRP1/2, iron regulatory protein 1/2; ISC, iron-sulfur cluster; LIP, labile iron pool; LOXs, lipoxygenases; LPCAT3, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; MUFA, monounsaturated fatty acid; NCOA 4, nuclear receptor coactivator 4; NFS1, nitrogen fixation 1; NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2; PCBP2, Poly(rC)-binding Protein 2; PKCβII, protein kinase C βII; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acid; SP1, specificity protein 1; STEAP3, six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate 3; TF, transferrin; TFRC, transferrin receptor protein; YAP1, Yes associated protein 1. This diagram was drawn by Figdraw (www.figdraw.com)