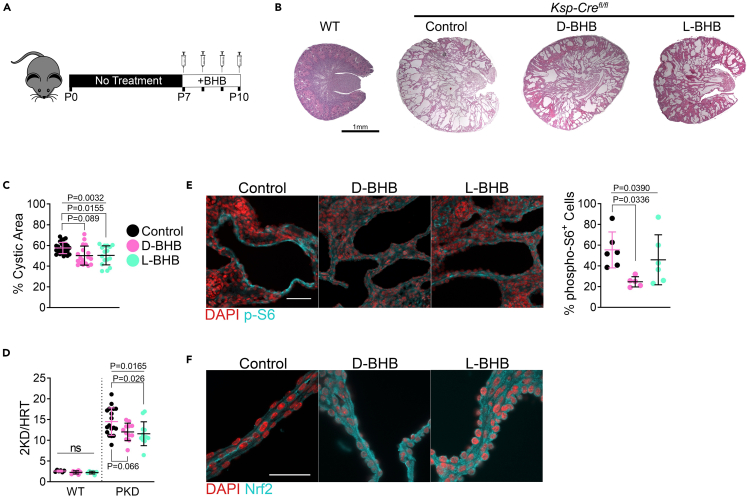
Figure 7.
Parenteral BHB administration ameliorates disease progression in a juvenile orthologous mouse model
(A) Schematic of experimental design for parenteral BHB administration in neonatal Pkd1-Ksp:Cre mice.
(B) Hematoxylin and eosin-stained kidneys from P10 wild-type or Pkd1fl/fl-Ksp:Cre control, D-BHB, or L-BHB injected mice. Scale = 1mm.
(C) Cystic area of all kidneys collected from P10 control, D-BHB, or L-BHB treated wild-type and Pkd1fl/fl-Ksp:Cre mice.
(D) 2–kidney-to-heart ratio from P10 control, D-BHB, or L-BHB-treated wild-type and Pkd1fl/fl-Ksp:Cre mice.
(E) Immunofluorescence of phospho-S6235/236 and quantification of cytoplasmic phospho-S6235/236 within cystic epithelia in P10 control, D-BHB, and L-BHB-treated Pkd1fl/fl-Ksp:Cre mice kidneys. Scale = 50μm.
(F) Immunofluorescence of Nrf2 in P10 control, D-BHB, and L-BHB-treated Pkd1fl/fl-Ksp:Cre mice kidneys. Scale = 50μm.
(See also Figure S9. Male and female mice were used for this experiment. One-way ANOVA followed by ad hoc Tukey’s test was used for multiple comparisons. Mean and standard deviations are shown).