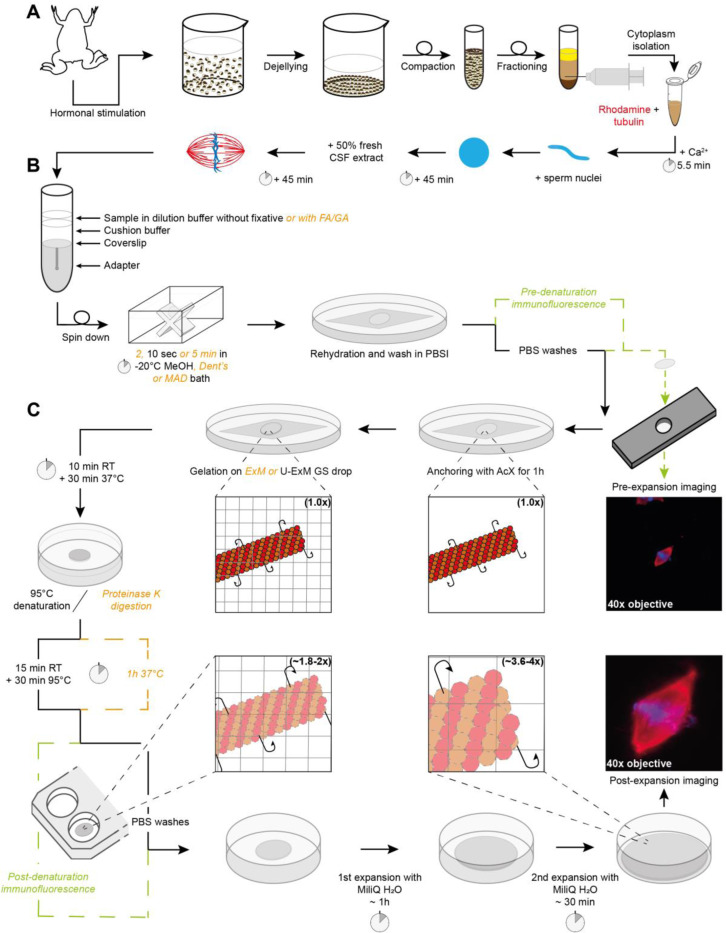
FIGURE 1:
Sample processing workflow for Expansion Microscopy of Xenopus egg extract spindles. (A) Preparation of egg extract spindles for expansion microscopy, including major steps of egg extract preparation and spindle assembly. (B) Sample in dilution buffer, with or without fixatives, is deposited on cushion buffer to spin-down spindles onto a coverslip placed at the top of the adapter. Following the centrifugation, the coverslip is immersed inside a bath of methanol or other fixative mixtures from 2 s to 5 min, and finally rehydrated in PBSI. (C) Expansion microscopy-specific steps from anchoring and gelation to disruption and expansion. Right images show the same spindle before (top) and after (bottom) expansion with rhodamine-labeled tubulin in red and DNA in blue. Note that immunofluorescence for pre-expansion imaging is performed after sample fixation and prior to anchoring and that immunofluorescence for post-expansion imaging is done after disruption and prior to expansion for imaging. If these steps are not performed, they are replaced by PBS washes. (CSF: cytostatic factor-arrested; FA: Formaldehyde; MeOH: Methanol; Dent’s: mix of methanol and DMSO; MAD: mix of methanol, acetone and DMSO; PBSI: PBS 0.1% IGEPAL® CA-630; AcX: 6-((acryloyl) amino) hexanoic acid, succinimidyl ester; ExM: Expansion Microscopy; U-ExM: Ultrastructure ExM; RT: room temperature).