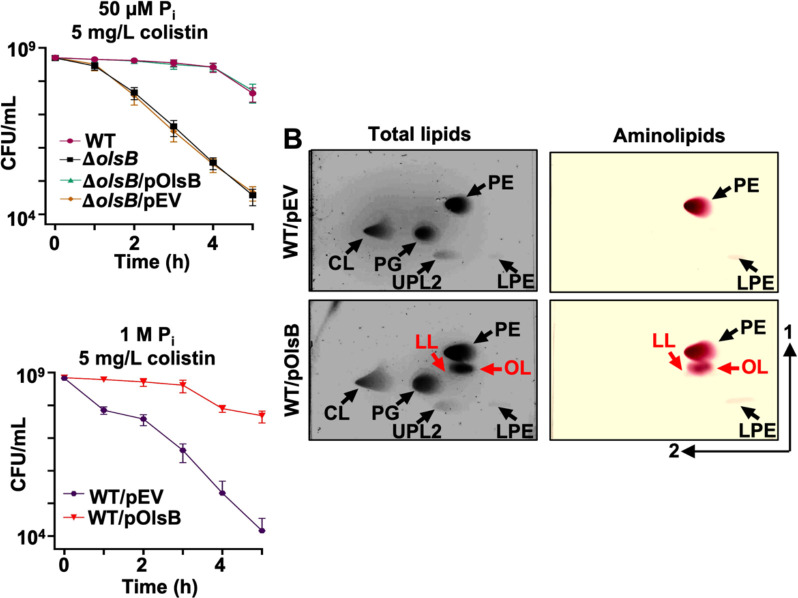
Figure 4: Aminolipids promote colistin tolerance in A. baumannii.
A. Colistin-dependent killing in wild type and ΔolsB mutant strains under phosphate limitation (n = 3). Error bars indicate standard deviation. Wild type (WT) strains carrying pOlsB or empty vector were subjected to 5 mg/L colistin exposure over time. CFU/mL were calculated every 0.5 h. B. Total lipids were extracted using the Bligh and Dyer method and separated using 2D thin-layer chromatography. Lipids were stained with sulfuric acid (left). Aminolipids were stained using ninhydrin (right). Specific lipids are labelled: PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PG, phosphatidylglycerol; CL, cardiolipin; LPE, lyso-phosphatidylethanolamine; LL, lysine lipid; OL, ornithine lipid; U3, unknown lipid 3. OL and LL are labelled in red. C. Colistin-dependent kill curves (left) and growth rate analysis (right) in wild type expressing empty vector (pEV) or pOlsB under high phosphate conditions (n = 3). Error bars indicate standard deviation.