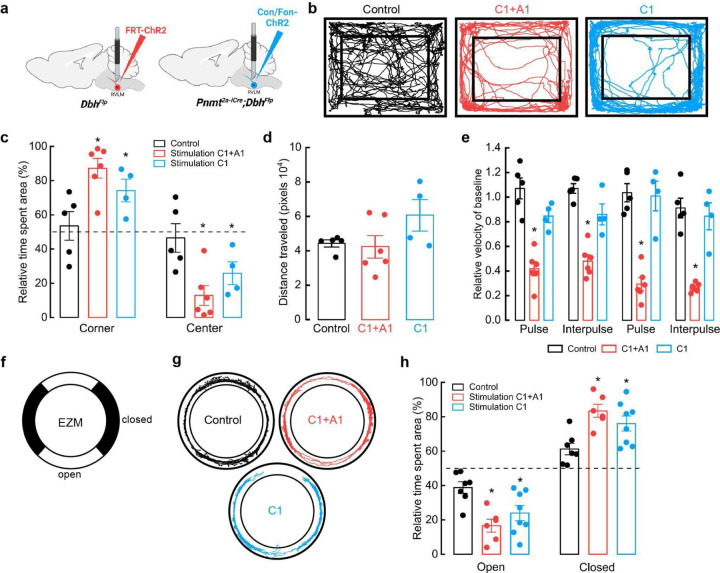
Figure 3. Optogenetic activation of C1 neurons enhances anxiety-like behaviors.
a, Strategy for targeted viral expression of channelrhodopsin (ChR2) in C1+A1 (red) or C1 (blue) neurons and optic fiber implantation in RVLM. b, Representative cumulative trajectories (10 min) in the open field test (OFT) for control (black), C1+A1 (red) and C1 (blue) mice. c, Average percentage of time spent in the corners or center of the OFT. d, Average total distance traveled in the OFT. e, Average change in velocity relative to baseline during (pulse) or between (interpulse) periods of optogenetic stimulation (20 Hz, 20 ms pulse width, for 30 s, 30 s rest). f, Schematic of elevated zero maze (EZM). g, Representative cumulative trajectories (10 min) in the EZM while optogenetically stimulated (20 Hz, 20 ms pulse width, for 30 s, 30 s rest, 5 min total) for control (black), C1+A1 (red) and C1 (blue) mice. h, Average time spent in the open and closed areas of the EZM. Control n=5, C1+A1 n= 6, C1 n=4 animals for b-e; Control n=7, C1+A1 n= 6, C1 n=8 for g, h. Data represents mean ± SEM. *p<0.05 vs control, Kruskal Wallis test with Dunn’s post hoc test.